Magnetic resonance imaging spectrum of succinate dehydrogenase-related infantile leukoencephalopathy
- PMID: 26642834
- PMCID: PMC5712845
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.24572
Magnetic resonance imaging spectrum of succinate dehydrogenase-related infantile leukoencephalopathy
Erratum in
-
Correction to Helman et al (2016) MRI spectrum of SDH deficiency-related infantile leukoencephalopathy.Ann Neurol. 2018 Sep;84(3):481. doi: 10.1002/ana.25296. Ann Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30246903 No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient leukoencephalopathy is a complex II-related mitochondrial disorder for which the clinical phenotype, neuroimaging pattern, and genetic findings have not been comprehensively reviewed.
Methods: Nineteen individuals with succinate dehydrogenase deficiency-related leukoencephalopathy were reviewed for neuroradiological, clinical, and genetic findings as part of institutional review board-approved studies at Children's National Health System (Washington, DC) and VU University Medical Center (Amsterdam, the Netherlands).
Results: All individuals had signal abnormalities in the central corticospinal tracts and spinal cord where imaging was available. Other typical findings were involvement of the cerebral hemispheric white matter with sparing of the U fibers, the corpus callosum with sparing of the outer blades, the basis pontis, middle cerebellar peduncles, and cerebellar white matter, and elevated succinate on magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). The thalamus was involved in most studies, with a predilection for the anterior nucleus, pulvinar, and geniculate bodies. Clinically, infantile onset neurological regression with partial recovery and subsequent stabilization was typical. All individuals had mutations in SDHA, SDHB, or SDHAF1, or proven biochemical defect.
Interpretation: Succinate dehydrogenase deficiency is a rare leukoencephalopathy, for which improved recognition by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in combination with advanced sequencing technologies allows noninvasive diagnostic confirmation. The MRI pattern is characterized by cerebral hemispheric white matter abnormalities with sparing of the U fibers, corpus callosum involvement with sparing of the outer blades, and involvement of corticospinal tracts, thalami, and spinal cord. In individuals with infantile regression and this pattern of MRI abnormalities, the differential diagnosis should include succinate dehydrogenase deficiency, in particular if MRS shows elevated succinate.
© 2016 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
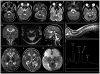

References
-
- van der Knaap MS, Valk J, de Neeling N, Nauta JJ. Pattern recognition in magnetic resonance imaging of white matter disorders in children and young adults. Neuroradiology. 1991;33(6):478–93. - PubMed
-
- Vanderver A, Simons C, Helman G, et al. Whole exome sequencing in a cohort of patients with unresolved central nervous system white matter abnormalities. 2015 In Press.
-
- van der Knaap MS, Breiter SN, Naidu S, Hart AA, Valk J. Defining and categorizing leukoencephalopathies of unknown origin: MR imaging approach. Radiology. 1999 Oct;213(1):121–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

