ScanIndel: a hybrid framework for indel detection via gapped alignment, split reads and de novo assembly
- PMID: 26643039
- PMCID: PMC4671222
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-015-0251-2
ScanIndel: a hybrid framework for indel detection via gapped alignment, split reads and de novo assembly
Abstract
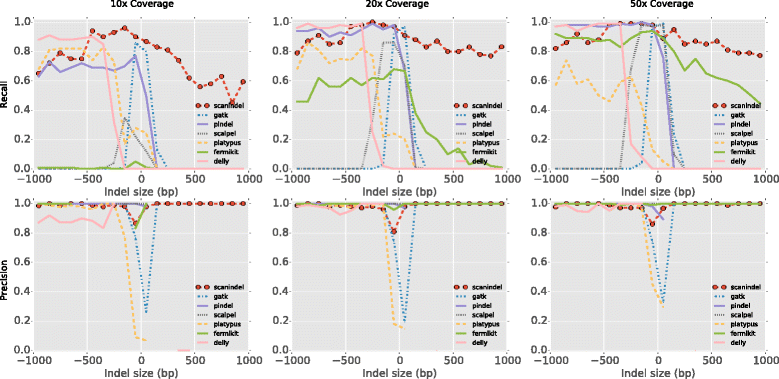
Comprehensive identification of insertions/deletions (indels) across the full size spectrum from second generation sequencing is challenging due to the relatively short read length inherent in the technology. Different indel calling methods exist but are limited in detection to specific sizes with varying accuracy and resolution. We present ScanIndel, an integrated framework for detecting indels with multiple heuristics including gapped alignment, split reads and de novo assembly. Using simulation data, we demonstrate ScanIndel's superior sensitivity and specificity relative to several state-of-the-art indel callers across various coverage levels and indel sizes. ScanIndel yields higher predictive accuracy with lower computational cost compared with existing tools for both targeted resequencing data from tumor specimens and high coverage whole-genome sequencing data from the human NIST standard NA12878. Thus, we anticipate ScanIndel will improve indel analysis in both clinical and research settings. ScanIndel is implemented in Python, and is freely available for academic use at https://github.com/cauyrd/ScanIndel.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The challenge of detecting indels in bacterial genomes from short-read sequencing data.J Biotechnol. 2017 May 20;250:11-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.02.026. Epub 2017 Mar 4. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28267569
-
IMSindel: An accurate intermediate-size indel detection tool incorporating de novo assembly and gapped global-local alignment with split read analysis.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 4;8(1):5608. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23978-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29618752 Free PMC article.
-
ABRA: improved coding indel detection via assembly-based realignment.Bioinformatics. 2014 Oct;30(19):2813-5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu376. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24907369 Free PMC article.
-
The bioinformatics tools for the genome assembly and analysis based on third-generation sequencing.Brief Funct Genomics. 2019 Feb 14;18(1):1-12. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ely037. Brief Funct Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30462154 Review.
-
State of the art de novo assembly of human genomes from massively parallel sequencing data.Hum Genomics. 2010 Apr;4(4):271-7. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-4-4-271. Hum Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20511140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EBV-negative monomorphic B-cell post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders are pathologically distinct from EBV-positive cases and frequently contain TP53 mutations.Mod Pathol. 2016 Oct;29(10):1200-11. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2016.130. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Mod Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27443517
-
Primary mucosal melanomas of the head and neck are characterised by overexpression of the DNA mutating enzyme APOBEC3B.Histopathology. 2023 Mar;82(4):608-621. doi: 10.1111/his.14843. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Histopathology. 2023. PMID: 36416305 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent Loss of ABC Transporter Genes From Clostridioides difficile Genomes Is Associated With Impaired Tyrosine Uptake and p-Cresol Production.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 8;9:901. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00901. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29867812 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution mapping reveals the mechanism and contribution of genome insertions and deletions to RNA virus evolution.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug;120(31):e2304667120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2304667120. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37487061 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a microfluidics-based next generation sequencing assay for clinical oncology diagnostics.Ann Transl Med. 2018 May;6(9):162. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.05.07. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29911110 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

