The interaction of lubricin/proteoglycan 4 (PRG4) with toll-like receptors 2 and 4: an anti-inflammatory role of PRG4 in synovial fluid
- PMID: 26643105
- PMCID: PMC4672561
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0877-x
The interaction of lubricin/proteoglycan 4 (PRG4) with toll-like receptors 2 and 4: an anti-inflammatory role of PRG4 in synovial fluid
Abstract
Background: Lubricin/proteoglycan-4 (PRG4) is a mucinous glycoprotein secreted by synovial fibroblasts and superficial zone chondrocytes. PRG4 has a homeostatic multifaceted role in the joint. PRG4 intra-articular treatment retards progression of cartilage degeneration in pre-clinical posttraumatic osteoarthritis models. The objective of this study is to evaluate the binding of recombinant human PRG4 (rhPRG4) and native human PRG4 (nhPRG4) to toll-like receptors 2 and 4 (TLR2 and TLR4) and whether this interaction underpins a PRG4 anti-inflammatory role in synovial fluid (SF) from patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
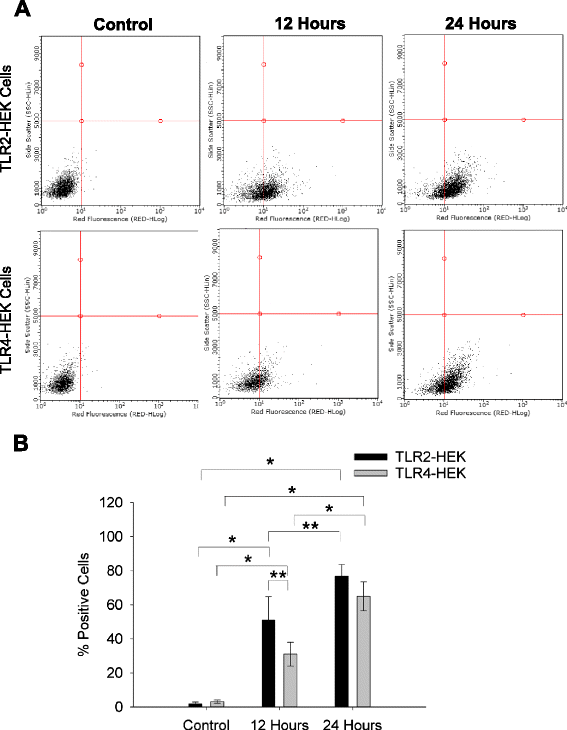
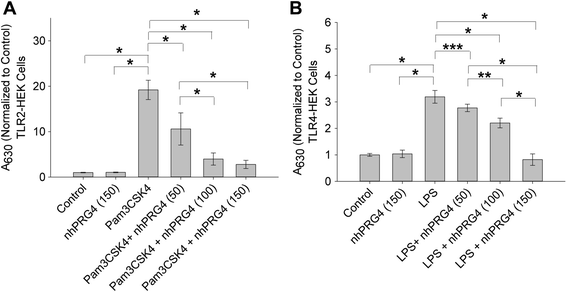
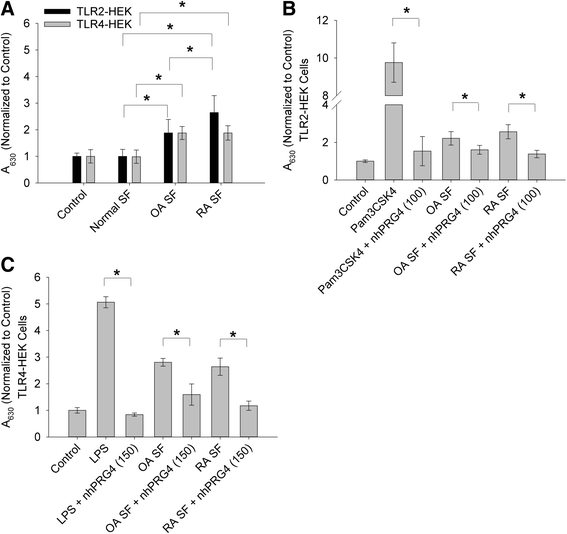
Methods: rhPRG4 and nhPRG4 binding to TLR2 and TLR4 was evaluated using a direct enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Association of rhPRG4 with TLR2 and TLR4 overexpressing human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells was studied by flow cytometry. Activation of TLR2 and TLR4 on HEK cells by agonists Pam3CSK4 and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was studied in the absence or presence of nhPRG4 at 50, 100 and 150 μg/ml. Activation of TLR2 and TLR4 by OA SF and RA SF and the effect of nhPRG4 SF treatment on receptor activation was assessed. PRG4 was immunoprecipitated from pooled OA and RA SF. TLR2 and TLR4 activation by pooled OA and RA SF with or without PRG4 immunoprecipitation was compared.
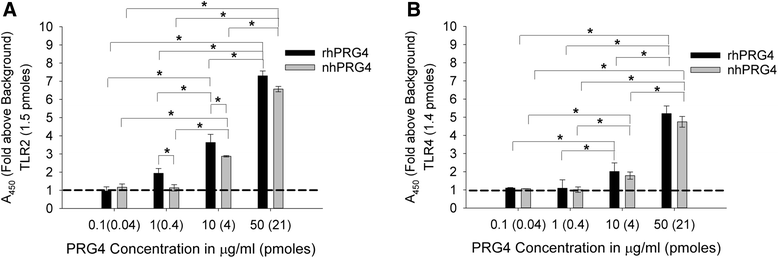
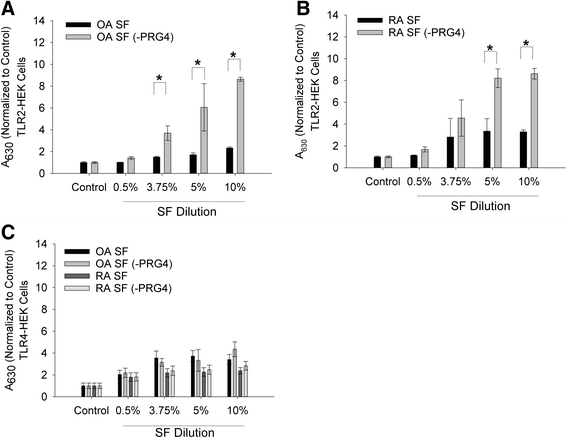
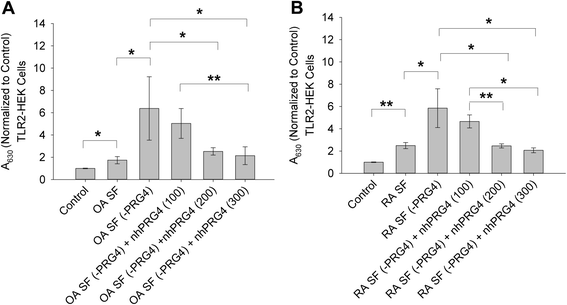
Results: rhPRG4 and nhPRG4 exhibited concentration-dependent binding to TLR2 and TLR4. rhPRG4 associated with TLR2- and TLR4-HEK cells in a time-dependent manner. Co-incubation of nhPRG4 (50, 100 and 150 μg/ml) and Pam3CSK4 or LPS reduced TLR2 or TLR4 activation compared to Pam3CSK4 or LPS alone (p <0.05). OA SF and RA SF activated TLR2 and TLR4 and nhPRG4 treatment reduced SF-induced receptor activation (p <0.001). PRG4 depletion by immunoprecipitation significantly increased TLR2 activation by OA SF and RA SF (p <0.001).
Conclusion: PRG4 binds to TLR2 and TLR4 and this binding mediates a novel anti-inflammatory role for PRG4.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The autocrine role of proteoglycan-4 (PRG4) in modulating osteoarthritic synoviocyte proliferation and expression of matrix degrading enzymes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 May 8;19(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1301-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28482921 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant human proteoglycan-4 reduces phagocytosis of urate crystals and downstream nuclear factor kappa B and inflammasome activation and production of cytokines and chemokines in human and murine macrophages.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Aug 29;20(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1693-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30157934 Free PMC article.
-
Lubricin/Proteoglycan 4 Binding to CD44 Receptor: A Mechanism of the Suppression of Proinflammatory Cytokine-Induced Synoviocyte Proliferation by Lubricin.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Jun;67(6):1503-13. doi: 10.1002/art.39087. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25708025 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of lubricin: near frictionless joint motion.Matrix Biol. 2014 Oct;39:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 25172828 Review.
-
Regulatory Mechanisms of Prg4 and Gdf5 Expression in Articular Cartilage and Functions in Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 23;23(9):4672. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094672. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Camptodactyly-Arthropathy-Coxa Vara-Pericarditis Syndrome Resembling Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Single-Center Experience from Southern Turkey.Mol Syndromol. 2021 Apr;12(2):112-117. doi: 10.1159/000513111. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Mol Syndromol. 2021. PMID: 34012381 Free PMC article.
-
CD39+CD55- Fb Subset Exhibits Myofibroblast-Like Phenotype and Is Associated with Pain in Osteoarthritis of the Knee.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 14;11(11):3047. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113047. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38002046 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics based markers of clinical pain severity in juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2022 Jan 15;20(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12969-022-00662-1. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2022. PMID: 35033099 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-articular Recombinant Human Proteoglycan 4 Mitigates Cartilage Damage After Destabilization of the Medial Meniscus in the Yucatan Minipig.Am J Sports Med. 2017 Jun;45(7):1512-1521. doi: 10.1177/0363546516686965. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Am J Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28129516 Free PMC article.
-
Quadruped Gait and Regulation of Apoptotic Factors in Tibiofemoral Joints following Intra-Articular rhPRG4 Injection in Prg4 Null Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 12;23(8):4245. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084245. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jay GD, Britt DE, Cha CJ. Lubricin is a product of megakaryocyte stimulating factor gene expression by human synovial fibroblasts. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(3):594–600. - PubMed
-
- Jay GD, Tantravahi U, Britt DE, Barrach HJ, Cha CJ. Homology of lubricin and superficial zone protein (SZP): products of megakaryocyte stimulating factor (MSF) gene expression by human synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes localized to chromosome 1q25. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(4):677–87. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(00)00040-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Flannery CR, Hughes CE, Schumacher BL, Tudor D, Aydelotte MB, Kuettner KE, et al. Articular cartilage superficial zone protein (SZP) is homologous to megakaryocyte stimulating factor precursor and is a multifunctional proteoglycan with potential growth-promoting cytoprotective, and lubricating properties in cartilage metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;254(3):535–41. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.0104. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

