Comparative study of two doses of intrathecal dexmedetomidine as adjuvant with low dose hyperbaric bupivacaine in ambulatory perianal surgeries: A prospective randomised controlled study
- PMID: 26644612
- PMCID: PMC4645353
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5049.167485
Comparative study of two doses of intrathecal dexmedetomidine as adjuvant with low dose hyperbaric bupivacaine in ambulatory perianal surgeries: A prospective randomised controlled study
Abstract
Background and aims: Dexmedetomidine (DMT), as intrathecal adjuvant has been shown to successfully prolong duration of analgesia but delay the motor recovery. Hence, this study was designed to find out the dose of DMT which can provide satisfactory analgesia without prolonging motor block.
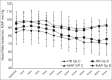
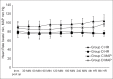
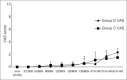
Methods: A total of 50 patients scheduled for elective perianal surgeries were randomly allocated to Groups C or D (n = 25). Group D received hyperbaric bupivacaine 0.5% 4 mg + DMT 5 μg and Group C received hyperbaric bupivacaine 0.5% 4 mg + DMT 3 μg intrathecally. Onset and duration of sensory and motor blockade, duration of analgesia, time for ambulation and first urination were recorded. Adverse effects if any were noted.
Results: Demographic characters, duration of surgery were comparable. The onset of sensory block to S1 was 9.61 ± 5.53 min in Group C compared to 7.69 ± 4.80 min in Group D (P = 0.35). Duration of sensory (145.28 ± 83.17 min - C, 167.85 ± 93.75 min - D, P = 0.5) and motor block (170.53 ± 73.44 min - C, 196.14 ± 84.28 min, P = 0.39) were comparable. Duration of analgesia (337.86 ± 105.11 min - C, 340.78 ± 101.81 min - D, P = 0.9) and time for ambulation (252.46 ± 93.72 min - C, 253.64 ± 88.04 min - D, P = 0.97) were also comparable. One patient in each group had urinary retention requiring catheterization. No other side effects were observed.
Conclusion: Intrathecal DMT 3 μg dose does not produce faster ambulation compared to intrathecal DMT 5 μg though it produces comparable duration of analgesia for perianal surgeries.
Keywords: Ambulatory; dexmedetomidine; intrathecal; motor block; perianal surgeries.
Figures
References
-
- Gudaityte J, Marchertiene I, Karbonskiene A, Saladzinskas Z, Tamelis A, Toker I, et al. Low-dose spinal hyperbaric bupivacaine for adult anorectal surgery: A double-blinded, randomized, controlled study. J Clin Anesth. 2009;21:474–81. - PubMed
-
- Kim JE, Kim NY, Lee HS, Kil HK. Effects of intrathecal dexmedetomidine on low-dose bupivacaine spinal anesthesia in elderly patients undergoing transurethral prostatectomy. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36:959–65. - PubMed
-
- Awad IT, Cheung JJ, Al-Allaq Y, Conroy PH, McCartney CJ. Low-dose spinal bupivacaine for total knee arthroplasty facilitates recovery room discharge: A randomized controlled trial. Can J Anaesth. 2013;60:259–65. - PubMed
-
- Carr DB, Cousins MJ. Spinal route of analgesia. In: Cousins MJ, Carr DB, Horlocker TT, Bridenbaugh PO, editors. Cousins and Bridenbaugh's Neural Blockade in Clinical Anaesthesia and Pain Medicine. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lipincott Williams and Wilkins; 2009. pp. 886–95.
-
- Eid HE, Shafie MA, Youssef H. Dose-related prolongation of hyperbaric bupivacaine spinal anesthesia by dexmedetomidine. Ain Shams J Anesthesiol. 2011;4:83–95.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources