'Degraded' RNA profiles in Arthropoda and beyond
- PMID: 26644977
- PMCID: PMC4671170
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.1436
'Degraded' RNA profiles in Arthropoda and beyond
Abstract
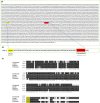
The requirement for high quality/non-degraded RNA is essential for an array of molecular biology analyses. When analysing the integrity of rRNA from the barnacle Lepas anatifera (Phylum Arthropoda, Subphylum Crustacea), atypical or sub-optimal rRNA profiles that were apparently degraded were observed on a bioanalyser electropherogram. It was subsequently discovered that the rRNA was not degraded, but arose due to a 'gap deletion' (also referred to as 'hidden break') in the 28S rRNA. An apparent excision at this site caused the 28S rRNA to fragment under heat-denaturing conditions and migrate along with the 18S rRNA, superficially presenting a 'degraded' appearance. Examination of the literature showed similar observations in a small number of older studies in insects; however, reading across multiple disciplines suggests that this is a wider issue that occurs across the Animalia and beyond. The current study shows that the 28S rRNA anomaly goes far beyond insects within the Arthropoda and is widespread within this phylum. We confirm that the anomaly is associated with thermal conversion because gap-deletion patterns were observed in heat-denatured samples but not in gels with formaldehyde-denaturing.
Keywords: Bioanalyser; Degraded rNA; Denaturing; Gap deletion; Hidden break; Taxonomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Insects' RNA Profiling Reveals Absence of "Hidden Break" in 28S Ribosomal RNA Molecule of Onion Thrips, Thrips tabaci.J Nucleic Acids. 2015;2015:965294. doi: 10.1155/2015/965294. Epub 2015 Feb 12. J Nucleic Acids. 2015. PMID: 25767721 Free PMC article.
-
RNA profile diversity across arthropoda: guidelines, methodological artifacts, and expected outcomes.Biol Methods Protoc. 2018 Dec 15;3(1):bpy012. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpy012. eCollection 2018. Biol Methods Protoc. 2018. PMID: 32161805 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of introduction of the hidden break into the 28S rRNA of insects: implication based on structural studies.Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6393-401. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6393. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986. PMID: 3018670 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of gap region in 28S rRNA molecules in brine shrimp Artemia parthenogenetica and planarian Dugesia japonica.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012 Apr;77(4):411-7. doi: 10.1134/S000629791204013X. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012. PMID: 22809161
-
Evolution of ribosomal RNA.Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1977;58(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(77)90116-x. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1977. PMID: 400949 Review.
Cited by
-
Data on SSR markers and SNPs filtered from transcriptome of Parvocalanus crassirostris.Data Brief. 2023 Jul 28;50:109449. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2023.109449. eCollection 2023 Oct. Data Brief. 2023. PMID: 37593181 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the replication of a plant rhabdovirus in its arthropod mite vector.Virus Res. 2025 Jan;351:199522. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199522. Epub 2025 Jan 4. Virus Res. 2025. PMID: 39732175 Free PMC article.
-
The β-oxidation pathway is downregulated during diapause termination in Calanus copepods.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 13;9(1):16686. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53032-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31723179 Free PMC article.
-
Trophic Position of the White Worm (Enchytraeus albidus) in the Context of Digestive Enzyme Genes Revealed by Transcriptomics Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 25;25(9):4685. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094685. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731903 Free PMC article.
-
Computational discovery of hidden breaks in 28S ribosomal RNAs across eukaryotes and consequences for RNA Integrity Numbers.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 20;9(1):19477. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55573-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31863008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gillespie JJ, Johnston JS, Cannone JJ, Gutell RR. Characteristics of the nuclear (18S, 5.8S, 28S and 5S) and mitochondrial (12S and 16S) rRNA genes of Apis mellifera (Insecta: Hymenoptera): structure, organization, and retrotransposable elements. Insect Molecular Biology. 2006;15(5):657–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2006.00689.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

