Risk Factors for Early-Onset and Very-Early-Onset Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Pancreatic Cancer Case-Control Consortium (PanC4) Analysis
- PMID: 26646264
- PMCID: PMC4710562
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000392
Risk Factors for Early-Onset and Very-Early-Onset Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Pancreatic Cancer Case-Control Consortium (PanC4) Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: While pancreatic cancer (PC) most often affects older adults, to date, there has been no comprehensive assessment of risk factors among PC patients younger than 60 years.
Methods: We defined early-onset PC (EOPC) and very-early-onset PC (VEOPC) as diagnosis of PC in patients younger than 60 and 45 years, respectively. We pooled data from 8 case-control studies, including 1954 patients with EOPC and 3278 age- and sex-matched control subjects. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify associations with EOPC and VEOPC.
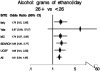
Results: Family history of PC, diabetes mellitus, smoking, obesity, and pancreatitis were associated with EOPC. Alcohol use equal to or greater than 26 g daily also was associated with increased risk of EOPC (odds ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-1.84), and there appeared to be a dose- and age-dependent effect of alcohol on risk. The point estimate for risk of VEOPC was an odds ratio of 2.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.17-4.09).
Conclusions: The established risk factors for PC, including smoking, diabetes, family history of PC, and obesity, also apply to EOPC. Alcohol intake appeared to have an age-dependent effect; the strongest association was with VEOPC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- (IARC) IAfRoC. GLOBOCAN 2012: Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence in 2012. [Date accessed:October 1, 2014];2012 Available at: http://globocan.iarc.fr/default.aspx.
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Society AC, editor. Cancer Facts and Figures. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2014. [Date Accessed:October 1, 2014]. Available at: http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/cancerfactsfigures2...
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975-2010. [Date accessed Oct 1,2014]; Available at: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2010/
-
- Raimondi S, Maisonneuve P, Lohr JM, et al. Early onset pancreatic cancer: evidence of a major role for smoking and genetic factors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:1894–1897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 PC035136/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035136/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA74783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA109767/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA098889/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098889/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA97075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109767/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA089726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC-35136/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA89726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA102701/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA108370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA116303/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA59706/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098870/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA098870/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA102701/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA108370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA97075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
