Therapeutic potential of regulatory cytokines that target B cells
- PMID: 26647406
- PMCID: PMC4889880
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxv069
Therapeutic potential of regulatory cytokines that target B cells
Abstract
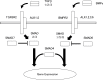
Autoreactive B cells play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by producing auto-antibodies and presenting antigens. Regulatory cytokines that simultaneously suppress multiple pathways have the potential to control autoreactive B cells. The generally inhibitory cytokine IL-10 may have a stimulatory effect on human B-cell survival and antibody production. TGF-β family cytokines can decrease or increase antibody production and can suppress B-cell proliferation and differentiation. In contrast to TGF-β1, which induces extensive fibrosis, TGF-β3 and bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP-6)/BMP-7 induce non-scarring wound healing and counteract tissue fibrosis. Therefore, TGF-β3 and BMP-6/BMP-7 may be clinically applicable as therapeutic cytokines that target B cells. Recent progress in protein engineering may enable us to generate novel biologic therapies based on TGF-β family cytokines.
Keywords: B cell; BMP; TGF-beta; regulatory T cell.
© The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2015. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Yan J. Harvey B. P. Gee R. J. Shlomchik M. J. and Mamula M. J. 2006. B cells drive early T cell autoimmunity in vivo prior to dendritic cell-mediated autoantigen presentation. J. Immunol. 177:4481. - PubMed
-
- Cheema G. S. Roschke V. Hilbert D. M. and Stohl W. 2001. Elevated serum B lymphocyte stimulator levels in patients with systemic immune-based rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 44:1313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

