Macula Densa Nitric Oxide Synthase 1β Protects against Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
- PMID: 26647426
- PMCID: PMC4978040
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015050515
Macula Densa Nitric Oxide Synthase 1β Protects against Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
Abstract
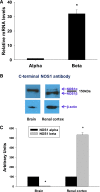
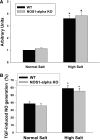
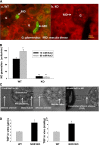
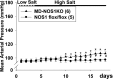
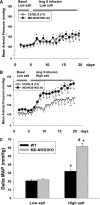
Nitric oxide (NO) is an important negative modulator of tubuloglomerular feedback responsiveness. We recently found that macula densa expresses α-, β-, and γ-splice variants of neuronal nitric oxide synthase 1 (NOS1), and NOS1β expression in the macula densa increases on a high-salt diet. This study tested whether upregulation of NOS1β expression in the macula densa affects sodium excretion and salt-sensitive hypertension by decreasing tubuloglomerular feedback responsiveness. Expression levels of NOS1β mRNA and protein were 30- and five-fold higher, respectively, than those of NOS1α in the renal cortex of C57BL/6 mice. Furthermore, macula densa NO production was similar in the isolated perfused juxtaglomerular apparatus of wild-type (WT) and nitric oxide synthase 1α-knockout (NOS1αKO) mice. Compared with control mice, mice with macula densa-specific knockout of all nitric oxide synthase 1 isoforms (MD-NOS1KO) had a significantly enhanced tubuloglomerular feedback response and after acute volume expansion, significantly reduced GFR, urine flow, and sodium excretion. Mean arterial pressure increased significantly in MD-NOS1KO mice (P<0.01) but not NOS1flox/flox mice fed a high-salt diet. After infusion of angiotensin II, mean arterial pressure increased by 61.6 mmHg in MD-NOS1KO mice versus 32.0 mmHg in WT mice (P<0.01) fed a high-salt diet. These results indicate that NOS1β is a primary NOS1 isoform expressed in the macula densa and regulates the tubuloglomerular feedback response, the natriuretic response to acute volume expansion, and the development of salt-sensitive hypertension. These findings show a novel mechanism for salt sensitivity of BP and the significance of tubuloglomerular feedback response in long-term control of sodium excretion and BP.
Keywords: NOS1; hypertension; macula densa; salt-sensitive; tubuloglomerular feedback.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Do You Want to Ditch Sodium? Meet Nitric Oxide Synthase 1β at the Macula Densa.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Aug;27(8):2217-8. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015121378. Epub 2016 Feb 22. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26903534 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Goormaghtigh N: Les segments neuro-myo-artériels juxtaglomérulaires du rein. Arch Biol (Liege) 43: 575–591, 1932
-
- Zimmerman KW: Ueber den bau des glomerulus der saeugerniere. Z Microskop Anat Forsch 32: 176–287, 1933
-
- Thurau K, Schnermann J: The sodium concentration in the macula densa cells as a regulating factor for glomerular filtration (micropuncture experiments). Klin Wochenschr 43: 410–413, 1965 - PubMed
-
- Liu R, Pittner J, Persson AE: Changes of cell volume and nitric oxide concentration in macula densa cells caused by changes in luminal NaCl concentration. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 2688–2696, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

