Dissociation between systemic and pulmonary anti-inflammatory effects of dexamethasone in humans
- PMID: 26647918
- PMCID: PMC4834593
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12857
Dissociation between systemic and pulmonary anti-inflammatory effects of dexamethasone in humans
Abstract
Aims: The local pulmonary inflammatory response has a different temporal and qualitative profile compared with the systemic inflammatory response. Although glucocorticoids substantially downregulate the systemic release of acute-phase mediators, it is not clear whether they have comparable inhibitory effects in the human lung compartment. Therefore, we compared the anti-inflammatory effects of a pure glucocorticoid agonist, dexamethasone, on bronchoalveolar lavage and blood cytokine concentrations in response to bronchially instilled endotoxin.
Methods: In this randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trial, 24 volunteers received dexamethasone or placebo and had endotoxin instilled into a lung segment and saline instilled into a contralateral segment, followed by bronchoalveolar lavage.
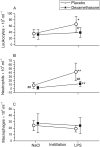
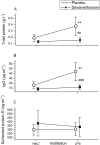
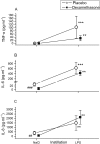
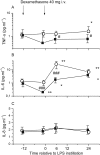
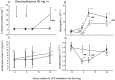
Results: Bronchially instilled endotoxin induced a local and systemic inflammatory response. Dexamethasone strongly blunted the systemic interleukin (IL) 6 and C-reactive protein release. In sharp contrast, dexamethasone left the local release of acute-phase mediators in the lungs virtually unchanged: bronchoalveolar lavage levels of IL-6 were only 18% lower and levels of IL-8 were even higher with dexamethasone compared with placebo, although the differences between treatments were not statistically significant (P = 0.07 and P = 0.08, respectively). However, dexamethasone had inhibitory effects on pulmonary protein extravasation and neutrophil migration.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated a remarkable dissociation between the systemic anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids and its protective effects on capillary leak on the one hand and surprisingly low anti-inflammatory effects in the lungs on the other.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; dexamethasone; lipopolysaccharide; lung inflammation; surfactant protein D.
© 2015 The Authors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Oliveira GP, Silva JD, Marques PS, Goncalves‐de‐Albuquerque CF, Santos HL, Vascocellos AP, Takiya CM, Morales MM, Pelosi P, Mocsai A, de Castro‐Faria‐Neto HC, Rocco PR. The effects of dasatinib in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome depend on dose and etiology. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015; 36: 1644–58. - PubMed
-
- Yi ES, Remick DG, Lim Y, Tang W, Nadzienko CE, Bedoya A, Yin S, Ulich TR. The intratracheal administration of endotoxin: X. Dexamethasone downregulates neutrophil emigration and cytokine expression in vivo . Inflammation 1996; 20: 165–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

