Identification of Genes Associated with Smad3-dependent Renal Injury by RNA-seq-based Transcriptome Analysis
- PMID: 26648110
- PMCID: PMC4673424
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17901
Identification of Genes Associated with Smad3-dependent Renal Injury by RNA-seq-based Transcriptome Analysis
Abstract
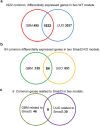
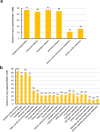
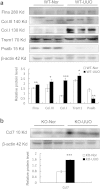
Transforming growth factor-β/Smad3 signaling plays a critical role in the process of chronic kidney disease (CKD), but targeting Smad3 systematically may cause autoimmune disease by impairing immunity. In this study, we used whole-transcriptome RNA-sequencing to identify the differential gene expression profile, gene ontology, pathways, and alternative splicing related to TGF-β/Smad3 in CKD. To explore common dysregulation of genes associated with Smad3-dependent renal injury, kidney tissues of Smad3 wild-type and knockout mice with immune (anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis) and non-immune (obstructive nephropathy)-mediated CKD were used for RNA-sequencing analysis. Totally 1922 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were commonly found in these CKD models. The up-regulated genes are inflammatory and immune response associated, while decreased genes are material or electron transportation and metabolism related. Only 9 common DEGs were found to be Smad3-dependent in two models, including 6 immunoglobulin genes (Ighg1, Ighg2c, Igkv12-41, Ighv14-3, Ighv5-6 and Ighg2b) and 3 metabolic genes (Ugt2b37, Slc22a19, and Mfsd2a). Our results identify transcriptomes associated with renal injury may represent a common mechanism for the pathogenesis of CKD and reveal novel Smad3 associated transcriptomes in the development of CKD.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang L. et al.. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet 379, 815–822 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Huang X. R. et al.. Smad3 mediates cardiac inflammation and fibrosis in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive cardiac remodeling. Hypertension 55, 1165–1171 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Lan H. Y. & Chung A. C. TGF-beta/Smad signaling in kidney disease. Semin Nephrol 32, 236–243 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

