Aflibercept Traps Galectin-1, an Angiogenic Factor Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy
- PMID: 26648523
- PMCID: PMC4673700
- DOI: 10.1038/srep17946
Aflibercept Traps Galectin-1, an Angiogenic Factor Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
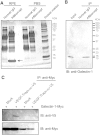
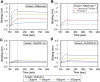
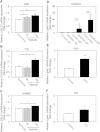
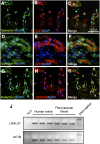
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A-driven angiogenesis contributes to various disorders including cancer and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Among several VEGF-A blockers clinically used is aflibercept, a chimeric VEGFR1/VEGFR2-based decoy receptor fused to the Fc fragment of IgG1 (i.e., VEGFR1/VEGFR2-Fc). Here, we revealed a novel anti-angiogenic function for aflibercept beyond its antagonism against VEGF family members. Immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry analyses identified galectin-1 as an aflibercept-interacting protein. Biolayer interferometry revealed aflibercept binding to galectin-1 with higher affinity than VEGFR1-Fc and VEGFR2-Fc, which was abolished by deglycosylation of aflibercept with peptide:N-glycosidase F. Retinal LGALS1/Galectin-1 mRNA expression was enhanced in vitro by hypoxic stimulation and in vivo by induction of diseases including diabetes. Galectin-1 immunoreactivity co-localized with VEGFR2 in neovascular tissues surgically excised from human eyes with PDR. Compared with non-diabetic controls, intravitreal galectin-1 protein levels were elevated in PDR eyes, showing no correlation with increased VEGF-A levels. Preoperative injection of bevacizumab, a monoclonal antibody to VEGF-A, reduced the VEGF-A, but not galectin-1, levels. Galectin-1 application to human retinal microvascular endothelial cells up-regulated VEGFR2 phosphorylation, which was eliminated by aflibercept. Our present findings demonstrated the neutralizing efficacy of aflibercept against galectin-1, an angiogenic factor associated with PDR independently of VEGF-A.
Figures

References
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285, 1182–1186 (1971). - PubMed
-
- Hicklin D. J. & Ellis L. M. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23, 1011–1027 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Hoeben A. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev 56, 549–580 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Adamis A. P. et al. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 118, 445–450 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor and age-related macular degeneration: from basic science to therapy. Nat Med 16, 1107–1111 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

