Minor burn management: potions and lotions
- PMID: 26648640
- PMCID: PMC4653976
- DOI: 10.18773/austprescr.2015.041
Minor burn management: potions and lotions
Abstract
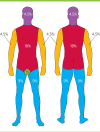
The first aid for burns is to run cold water over the burn for 20 minutes. This is effective for up to three hours after the injury. Assess the affected body surface area using the rule of nines. Consult a burn unit if more than 5% of the total body surface area is burnt in a child or if more than 10% in an adult. Extensive or deep burns and burns to special areas, such as the hands, should be referred. Chemical or electrical burns should also be assessed by a burn unit. For minor burns, antimicrobial dressings are recommended, but oral antibiotics should be avoided unless there are signs of infection. As burns are tetanus prone, check the patient's immunisation status. Burns that become infected or are slow to heal should be discussed with a burn unit. The burn unit can also provide advice if there are uncertainties about how to manage a patient.
Keywords: burns; dressings; first aid; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none declared
Figures
References
-
- Emergency Management of Severe Burns Manual. 17th ed. The Education Committee of the Australian and New Zealand Burns Association Ltd; 2013.
-
- Kim LH, Maze DA, Adams S, Guitonich S, Connolly S, Darton A, et al. Paediatric treadmill injuries: an increasing problem. Med J Aust 2009;191:516. - PubMed
-
- Jeremijenko L, Mott J, Wallis B, Kimble R. Paediatric treadmill friction injuries. J Paediatr Child Health 2009;45:310-2. - PubMed
-
- Knaysi GA, Crikelair GF, Cosman B. The role of nines: its history and accuracy. Plast Reconstr Surg 1968;41:560-3. - PubMed
-
- Australian and New Zealand Burn Association. ANZBA referral criteria. 2015. www.anzba.org.au/care/referral-criteria[cited 2015 Jul 1]
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials