Dynamics of quality of life improvement after floppy Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease
- PMID: 26649085
- PMCID: PMC4653267
- DOI: 10.5114/wiitm.2015.54187
Dynamics of quality of life improvement after floppy Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease
Abstract
Introduction: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) has a negative impact on global quality of life (QOL) of patients. In patients affected by GERD, laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is one of the most commonly performed laparoscopic procedures worldwide.
Aim: To prospectively analyze the dynamics of QOL as well as severity of pain in patients with GERD, before and after laparoscopic floppy Nissen fundoplication.
Material and methods: The study involved 104 consecutive patients operated on for GERD in whom laparoscopic floppy Nissen fundoplication was performed. QOL was assessed before surgery and 1, 3, 6, 12 and 24 months after. The following instruments were used: FACIT-G, FACIT-TS-G, GIQLI, GERD symptom scale.
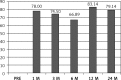
Results: It was found that symptom relief and quality of life improvement presented different dynamics in the postoperative course. Observations revealed relief of symptoms 1 month after surgery and improvement in QOL related to the gastrointestinal tract and pain 3 months after surgery. Global QOL increased significantly as late as 12 months after surgery.
Conclusions: Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a chronic disease of long duration, leading to impairment of quality of life. Patients, apart from typical symptoms of GERD, suffer from pain of significant severity. QOL improves significantly after surgery. Surgical treatment results in relief of GERD symptoms, which leads to gradual improvement of QOL.
Keywords: Nissen fundoplication; gastroesophageal reflux disease; quality of life.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication improves quality of life in patients with atypical symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux.Am Surg. 2003 Oct;69(10):833-8. Am Surg. 2003. PMID: 14570358
-
Does major depression in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease affect the outcome of laparoscopic antireflux surgery?Surg Endosc. 2003 Jan;17(1):55-60. doi: 10.1007/s00464-002-8504-8. Epub 2002 Sep 23. Surg Endosc. 2003. PMID: 12239650 Clinical Trial.
-
[Surgery of the hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux dinase, Nissen or Toupet?].Rozhl Chir. 2015 Dec;94(12):510-5. Rozhl Chir. 2015. PMID: 26767901 Czech.
-
Assessment of quality of life after laparoscopic GERD surgery in children: a prospective study.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 May;182(5):2005-2012. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-04897-2. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36872380 Review.
-
Effectiveness of laparoscopic fundoplication in relieving the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and eliminating antireflux medical therapy.Surg Endosc. 2003 Aug;17(8):1200-5. doi: 10.1007/s00464-002-8910-y. Epub 2003 May 13. Surg Endosc. 2003. PMID: 12739117 Review.
Cited by
-
Study of the prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms and the role of each in relation to the GERD Impact Scale, based on a population of patients admitted for laparoscopic surgery compared to a control group.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2018 Jun;13(2):199-211. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2018.75909. Epub 2018 May 22. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2018. PMID: 30002752 Free PMC article.
-
Ineffective Esophageal Motility in Patients with GERD is no Contraindication for Nissen Fundoplication.World J Surg. 2020 Jan;44(1):186-193. doi: 10.1007/s00268-019-05229-y. World J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31605176
-
Persistent dysphagia is a rare problem after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication.Surg Endosc. 2019 Apr;33(4):1196-1205. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6396-5. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Surg Endosc. 2019. PMID: 30171395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blomqvist A, Lonroth H, Dalenback J, Ruth M. Quality of life assessment after laparoscopic and open fundoplications. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1996;31:1052–8. - PubMed
-
- Prasad M, Rentz AM, Revicki DA. The impact of treatment for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease on health related quality of life. Pharmacoeconomics. 2003;21:769–90. - PubMed
-
- Woodcock SA, Watson DI, Lally C, et al. International Society for Disease of the Esophagus – Australasian Section. Quality of life following laparoscopic anterior 90 degrees versus Nissen fundoplication: results from a multicenter randomized trial. World J Surg. 2006;30:1856–63. - PubMed
-
- Kamolz T, Granderath FA, Pointner R. Does major depression in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease affect the outcome of laparoscopic antireflux surgery? Surg Endosc. 2003;17:55–60. - PubMed
-
- Kalinowska E. Quality of life and personality disorders in patients after surgical treatment of esophageal reflux disease. Postępy Nauk Medycznych. 2007;10:430–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
