Longxuetongluo Capsule Improves Erythrocyte Function against Lipid Peroxidation and Abnormal Hemorheological Parameters in High Fat Diet-Induced ApoE-/- Mice
- PMID: 26649134
- PMCID: PMC4663336
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/2603219
Longxuetongluo Capsule Improves Erythrocyte Function against Lipid Peroxidation and Abnormal Hemorheological Parameters in High Fat Diet-Induced ApoE-/- Mice
Abstract
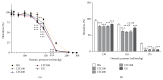
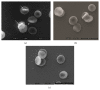
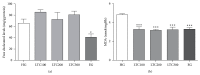
Chinese dragon's blood, the red resin of Dracaena cochinchinensis, one of the renowned traditional medicines, has been used to facilitate blood circulation and disperse blood stasis for thousands of years. Phenolic compounds are considered to be responsible for its main biological activities. In this study, total phenolic compounds of Chinese dragon's blood were made into capsule (Longxuetongluo Capsule, LTC) and their effects on the abnormal hemorheological properties were examined by high fat diet (HFD) induced ApoE-/- mice. Compared to the model group, LTC recovered the abnormal hemorheological parameters in HFD-induced ApoE-/- mice by reducing whole blood viscosity (WBV) at high rate and improving erythrocyte function. In conclusion, LTC could ameliorate erythrocyte deformability and osmotic fragility through the reduction of lipid peroxidation on plasma and erythrocyte membranes in HFD-induced ApoE-/- mice, which supported the traditional uses of Chinese dragon's blood as an effective agent for improving blood microcirculation in hypercholesterolemia.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Anti-atherosclerotic effect of Longxuetongluo Capsule in high cholesterol diet induced atherosclerosis model rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:793-801. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.141. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29112932
-
Effects of myakuryu on hemorheological characteristics and mesenteric microcirculation of rats fed with a high-fat diet.Biorheology. 2008;45(5):587-98. Biorheology. 2008. PMID: 19065007
-
Natural potential therapeutic agents of neurodegenerative diseases from the traditional herbal medicine Chinese dragon's blood.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Mar 28;152(3):508-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.032. Epub 2014 Feb 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24509154
-
Dragon's blood: botany, chemistry and therapeutic uses.J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Feb 12;115(3):361-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.10.018. Epub 2007 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18060708 Review.
-
Dragon's blood secretion and its ecological significance.Chemoecology. 2016;26:101-105. doi: 10.1007/s00049-016-0212-2. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Chemoecology. 2016. PMID: 27239099 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Erythrocyte membrane affinity chromatography, solid-phase extraction and UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS to screen active ingredients of Buyang Huanwu decoction.RSC Adv. 2019 Sep 17;9(50):29217-29224. doi: 10.1039/c9ra03447a. eCollection 2019 Sep 13. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35528420 Free PMC article.
-
Corydalis edulis Maxim. Promotes Insulin Secretion via the Activation of Protein Kinase Cs (PKCs) in Mice and Pancreatic β Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 16;7:40454. doi: 10.1038/srep40454. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28091547 Free PMC article.
-
Longxuetongluo Capsule protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress and MAPK-mediated mechanisms.J Adv Res. 2021 Feb 9;33:215-225. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.01.016. eCollection 2021 Nov. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 34603791 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of Longxue Tongluo Capsule on ischemic stroke rats revealed by LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics approach.Chin Herb Med. 2023 May 25;15(3):430-438. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.12.010. eCollection 2023 Jul. Chin Herb Med. 2023. PMID: 37538866 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Effects of Baoyuan Decoction on Dysfunctional Erythrocytes in High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemic ApoE-/- Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Mar 18;2019:5172480. doi: 10.1155/2019/5172480. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31089408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schechner V., Ben-Ami R., Hershcovici T., et al. Plasma dependent reduction in red blood cell aggregation after dextran sulfate low-density lipoprotein apheresis—implications for rheological studies. Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis. 2005;9(5):379–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-9987.2005.00317.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Koter M., Franiak I., Strychalska K., Broncel M., Chojnowska-Jezierska J. Damage to the structure of erythrocyte plasma membranes in patients with type-2 hypercholesterolemia. The International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 2004;36(2):205–215. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(03)00195-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

