Draft genome of Gemmata massiliana sp. nov, a water-borne Planctomycetes species exhibiting two variants
- PMID: 26649148
- PMCID: PMC4672568
- DOI: 10.1186/s40793-015-0103-0
Draft genome of Gemmata massiliana sp. nov, a water-borne Planctomycetes species exhibiting two variants
Abstract
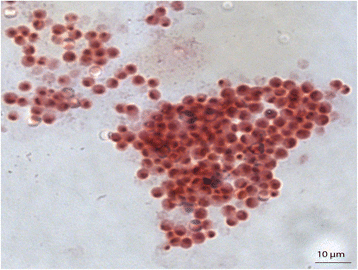
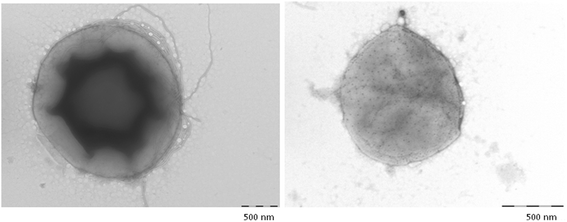
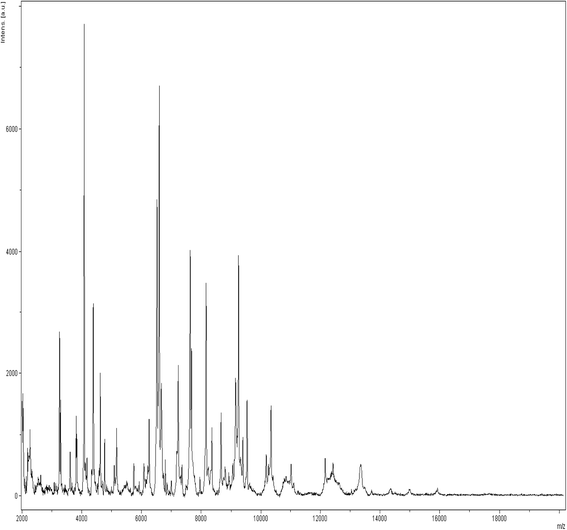
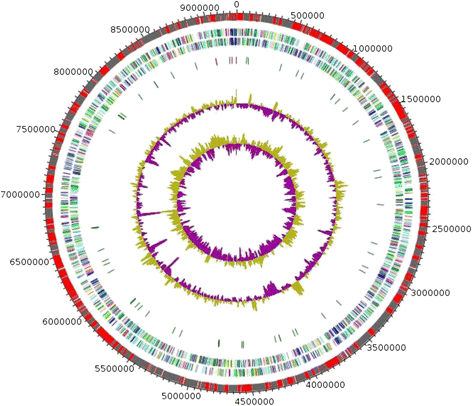
Gemmata massiliana is a new Planctomycetes bacterium isolated from a hospital water network in France, using a new culture medium. It is an aerobic microorganism with optimal growth at pH 8, at 30 °C and salinity ≤ 1.25 % NaCl. G. massiliana is resistant to β-lactam antibiotics, due to lack of peptidoglycan in its cell wall.G. massiliana shares a 97 % 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity with the nearest species, Gemmata obscuriglobus; and 99 % similarity with unnamed soil isolates. Its 9,249,437-bp genome consists in one chromosome and no detectable plasmid and has a 64.07 % G + C content, 32.94 % of genes encoding for hypothetical proteins. The genome contains an incomplete 19.6-kb phage sequence, 26 CRISPRs, 3 CAS and 15 clusters of secondary metabolites. G. massiliana genome increases knowledge of a poorly known world of bacteria.
Keywords: Culture; Gemmata; Gemmata massiliana; Gemmata obscuriglobus; Genome; Hospital water network; Planctomycetes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Escherichia coli Culture Filtrate Enhances the Growth of Gemmata spp.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 6;10:2552. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02552. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31781064 Free PMC article.
-
Improved culture of fastidious Gemmata spp. bacteria using marine sponge skeletons.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 12;9(1):11707. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48293-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31406238 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for detecting Gemmata spp. bacteremia in the microbiology laboratory.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Jan 8;11(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-3119-2. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 29310696 Free PMC article.
-
Gemmata species: Planctomycetes of medical interest.Future Microbiol. 2016 May;11:659-67. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2015-0001. Epub 2016 May 9. Future Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27158864 Review.
-
Intracellular compartmentation in planctomycetes.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005;59:299-328. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.59.030804.121258. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15910279 Review.
Cited by
-
Drancourtella massiliensis gen. nov., sp. nov. isolated from fresh healthy human faecal sample from South France.New Microbes New Infect. 2016 Feb 10;11:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2016.02.002. eCollection 2016 May. New Microbes New Infect. 2016. PMID: 27257490 Free PMC article.
-
Two-tiered mutualism improves survival and competitiveness of cross-feeding soil bacteria.ISME J. 2023 Nov;17(11):2090-2102. doi: 10.1038/s41396-023-01519-5. Epub 2023 Sep 22. ISME J. 2023. PMID: 37737252 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli Culture Filtrate Enhances the Growth of Gemmata spp.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 6;10:2552. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02552. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31781064 Free PMC article.
-
Improved culture of fastidious Gemmata spp. bacteria using marine sponge skeletons.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 12;9(1):11707. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48293-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31406238 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for detecting Gemmata spp. bacteremia in the microbiology laboratory.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Jan 8;11(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-3119-2. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 29310696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kulichevskaya IS, Pankratov TA, Dedysh SN. Detection of representatives of the Planctomycetes in Sphagnum peat bogs by molecular and cultivation approaches. Mikrobiologiia. 2006;75:329–335. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

