Animal Models in Studying Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
- PMID: 26649296
- PMCID: PMC4663287
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/178407
Animal Models in Studying Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
Abstract
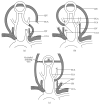
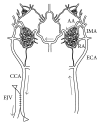
Brain arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an important cause of hemorrhagic stroke. The etiology is largely unknown and the therapeutics are controversial. A review of AVM-associated animal models may be helpful in order to understand the up-to-date knowledge and promote further research about the disease. We searched PubMed till December 31, 2014, with the term "arteriovenous malformation," limiting results to animals and English language. Publications that described creations of AVM animal models or investigated AVM-related mechanisms and treatments using these models were reviewed. More than 100 articles fulfilling our inclusion criteria were identified, and from them eight different types of the original models were summarized. The backgrounds and procedures of these models, their applications, and research findings were demonstrated. Animal models are useful in studying the pathogenesis of AVM formation, growth, and rupture, as well as in developing and testing new treatments. Creations of preferable models are expected.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Early rerupture of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: beware the progressive hemispheric swelling.Med Hypotheses. 2011 Apr;76(4):570-3. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2011.01.003. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Med Hypotheses. 2011. PMID: 21282013
-
Biology of vascular malformations of the brain.Stroke. 2009 Dec;40(12):e694-702. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.563692. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Stroke. 2009. PMID: 19834013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo intracerebral arteriovenous malformations and a review of the theories of their formation.Br J Neurosurg. 2018 Jun;32(3):305-311. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2018.1478060. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Br J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29873271 Review.
-
Embolization-induced angiogenesis in cerebral arteriovenous malformations.J Clin Neurosci. 2014 Nov;21(11):1866-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2014.04.010. Epub 2014 Jul 4. J Clin Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25001989 Review.
-
Vasospasm after arteriovenous malformation rupture.World Neurosurg. 2012 Sep-Oct;78(3-4):300-5. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2011.12.090. Epub 2011 Dec 28. World Neurosurg. 2012. PMID: 22381269 Review.
Cited by
-
A Microsurgical Arteriovenous Malformation Model on Saphenous Vessels in the Rat.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 4;11(11):2970. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11112970. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38001970 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging artifacts of Onyx and PHIL on conventional CT, cone-beam CT and MRI in an animal model.Interv Neuroradiol. 2018 Dec;24(6):693-701. doi: 10.1177/1591019918782692. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Interv Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 29973083 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNAs expression signatures of human brain arteriovenous malformation revealed by microarray.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(30):e11308. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011308. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30045256 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral macrophages in the development and progression of structural cerebrovascular pathologies.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Feb;44(2):169-191. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231217001. Epub 2023 Nov 24. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38000039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large animals in neurointerventional research: A systematic review on models, techniques and their application in endovascular procedures for stroke, aneurysms and vascular malformations.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 Mar;39(3):375-394. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19827446. Epub 2019 Feb 7. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019. PMID: 30732549 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

