Toward Independence: Resubmission Rate of Unfunded National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute R01 Research Grant Applications Among Early Stage Investigators
- PMID: 26650674
- PMCID: PMC4811707
- DOI: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001025
Toward Independence: Resubmission Rate of Unfunded National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute R01 Research Grant Applications Among Early Stage Investigators
Abstract
Purpose: The current, budget-driven low rate of National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding for biomedical research has raised concerns about new investigators' ability to become independent scientists and their willingness to persist in efforts to secure funding. The authors sought to determine resubmission rates for unfunded National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) early stage investigator (ESI) independent research grant (R01) applications and to identify resubmission predictors.
Method: The authors used a retrospective cohort study design and retrieved applications submitted in fiscal years 2010-2012 from NIH electronic research administrative sources. They defined ESI applicants as those who have received no prior R01 (or equivalent) funding and are within 10 years of completion of their terminal research degree or medical residency training. ESI applications at the NHLBI were eligible for special funding consideration if they scored above, but within 10 points of, the payline. The primary outcome was application resubmission after failing to secure funding with the first R01 submission.
Results: Over half of the unfunded applications were resubmitted. Some of these were discussed and "percentiled." Among percentiled applications, the only significant predictor of resubmission was the percentile score. Over half (59%) of the ESI R01 grants funded by NHLBI in fiscal years 2010-2012 had percentile scores above but within 10 points of the NHLBI payline, and benefited from the special funding considerations.
Conclusions: The only independent predictor of resubmission of NHLBI ESI R01 grant applications was percentile score; applicant demographics and institutional factors were not predictive of resubmission.
Figures
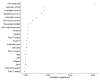

References
-
- Rockey S. A Look at Programs Targeting New Scientists. [Accessed September 30, 2015];Rock Talk. 2014 Apr 29; http://nexus.od.nih.gov/all/2014/04/29/a-look-at-programs-targeting-new-...
-
- Harris A. Young, Brilliant and Underfunded. [Accessed September 30, 2015];The New York Times. 2014 Oct 2; http://www.nytimes.com/2014/10/03/opinion/young-brilliant-and-underfunde....
-
- Harris R. When Scientists Give Up. [Accessed September 30, 2015];National Public Radio. 2014 Sep 9; http://www.npr.org/blogs/health/2014/09/09/345289127/when-scientists-giv....
-
- National Institutes of Health, Office of Extramural Research. [Accessed September 30, 2015];Encouraging Early Transition to Research Independence: Modifying the NIH New Investigator Policy to Identify Early Stage Investigators. NOT-OD-08-121. Updated August 12, 2009. http://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-08-121.html.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

