The tumor-suppressive and potential therapeutic functions of miR-34a in epithelial carcinomas
- PMID: 26652031
- PMCID: PMC4922263
- DOI: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1114102
The tumor-suppressive and potential therapeutic functions of miR-34a in epithelial carcinomas
Abstract
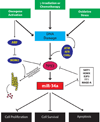
Introduction: Many RNA species have been identified as important players in the development of chronic diseases including cancer. Certain classes of regulatory RNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) have been investigated in such detail that bona fide tumor suppressive and oncogenic miRNAs have been identified. Because of this, there has been a major effort to therapeutically target these small RNAs. One in particular, a liposomal formulation of miR-34a (MRX34), has entered Phase I trials.
Areas covered: This review aims to summarize miRNA biology, its regulation within normal versus disease states and how it can be targeted therapeutically, with a particular emphasis on miR-34a. Understanding the complexity of a single miRNA will aid in the development of future RNA-based therapeutics for a broader range of chronic diseases.
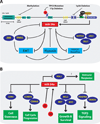
Expert opinion: The potential of miRNAs to be developed into anti-cancer therapeutics has become an increasingly important area of research. miR-34a is a tumor suppressive miRNA across many tumor types through its ability to inhibit cellular proliferation, invasion and tumor sphere formation. miR-34a also shows promise within certain in vivo solid tumor models. Finally, as miR-34a moves into clinical trials it will be important to determine if it can further sensitize tumors to certain chemotherapeutic agents.
Keywords: Biomarker; breast cancer; cancer; lung; miR-34; microRNA; therapy; treatment resistance; tumor suppressor.
Figures

References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
-
Bouchie A. First microRNA mimic enters clinic. Nat Biotechnol. Nature Publishing Group, a division of Macmillan Publishers Limited. All Rights Reserved. 2013;31:577. ** Of Considerable importance, discusses how MRX34 is the first-in-class miRNA replacement therapy for cancer
-
-
- Hermeking H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:193–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
