Effect of microbial cell preparation on renal profile and liver function among type 2 diabetics: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 26654906
- PMCID: PMC4676823
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-015-0952-5
Effect of microbial cell preparation on renal profile and liver function among type 2 diabetics: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The beneficial effect of probiotics on renal profile and liver function has been reported among patients with chronic kidney disease and fatty liver respectively. However, its effect on renal profile and liver function among type 2 diabetic individuals has not been fully understood. To investigate the effect of microbial cell preparation on renal profile and liver function tests among type 2 diabetic individuals.
Methods: A randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, controlled clinical trial was conducted on a total of 136 type 2 diabetics age 30-70 years old in a teaching hospital in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Subjects were randomly assigned to receive microbial cell preparation (N = 68) or a placebo (N = 68) for 12 weeks. The outcomes measured at baseline, week 6, and week 12 and included changes in renal profile (Sodium, Potassium, Urea, Creatinine, Glomerular Filtration Rate), and liver function tests (Albumin, Total Protein, Alkaline Phosphatase, Alanine Aminotransferase, Aspartate Aminotransferase). Intention to treat (ITT) analysis was performed on all the recruited subjects, while per protocol (PP) analysis was conducted on those who completed the trial with good compliance.
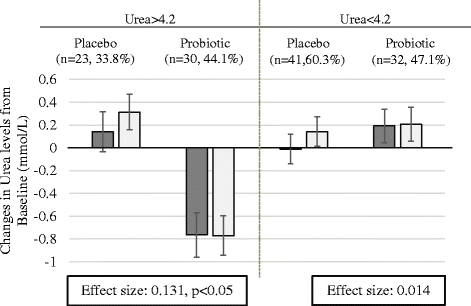
Result: The urea levels significantly declined in the probiotic group. Serum urea levels reduced from 4.26 mmol/L to 4.04 mmol/L in Probiotic Group while it increased in Placebo Group from 4.03 mmol/L to 4.24 mmol/L. These changes were significant between groups in ITT analysis (p = 0.018). Other parameters did not change significantly between groups.
Conclusion: 12 weeks supplementation with daily dosage of 6 × 10(10) Colony Forming Units of multi-strain microbial cell preparation significantly improved urea levels.
Trial registration: (
Clinical trials: # NCT01752803).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of multi-strain probiotics (multi-strain microbial cell preparation) on glycemic control and other diabetes-related outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Nutr. 2017 Jun;56(4):1535-1550. doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1199-8. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Eur J Nutr. 2017. PMID: 26988693 Clinical Trial.
-
A Multi-strain Probiotic Reduces the Fatty Liver Index, Cytokines and Aminotransferase levels in NAFLD Patients: Evidence from a Randomized Clinical Trial.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2018 Mar;27(1):41-49. doi: 10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.271.kby. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2018. PMID: 29557414 Clinical Trial.
-
Probiotic Supplementation in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial.J Ren Nutr. 2018 Jan;28(1):28-36. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2017.06.010. Epub 2017 Sep 6. J Ren Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28888762 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of continuous use of probiotics before liver transplantation: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Clin Nutr. 2017 Dec;36(6):1530-1539. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2017.04.021. Epub 2017 May 4. Clin Nutr. 2017. PMID: 28506447 Clinical Trial.
-
Liver and renal biochemical profiles of people with sickle cell disease in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies.Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 15;13(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02662-6. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39407336 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Obesity theranostics using nanoemulsions of probiotics and local herbs.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023 Oct;30(10):103790. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103790. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37680978 Free PMC article.
-
Can probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic supplementation modulate the gut-liver axis in type 2 diabetes? A narrative and systematic review of clinical trials.Front Nutr. 2022 Dec 1;9:1052619. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1052619. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36532552 Free PMC article.
-
The role of probiotics on microvascular complications of type-2 diabetes: Nephropathy and retinopathy.J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2024;16(2):65-76. doi: 10.34172/jcvtr.32877. Epub 2024 Jun 25. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2024. PMID: 39253347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota as a Source of Uremic Toxins.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;23(1):483. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010483. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35008909 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of bacterial probiotics on obesity, diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related variables: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.BMJ Open. 2019 Mar 30;9(3):e017995. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017995. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30928918 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

