Modeling synaptogenesis in schizophrenia and autism using human iPSC derived neurons
- PMID: 26655799
- PMCID: PMC6535231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.12.002
Modeling synaptogenesis in schizophrenia and autism using human iPSC derived neurons
Abstract
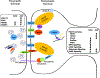
Schizophrenia (SCZ) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are genetically and phenotypically complex disorders of neural development. Human genetic studies, as well as studies examining structural changes at the cellular level, have converged on glutamatergic synapse formation, function, and maintenance as common pathophysiologic substrates involved in both disorders. Synapses as basic functional units of the brain are continuously modified by experience throughout life, therefore they are particularly attractive candidates for targeted therapy. Until recently we lacked a system to evaluate dynamic changes that lead to synaptic abnormalities. With the development of techniques to generate induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from patients, we are now able to study neuronal and synaptic development in cells from individual patients in the context of genetic changes conferring disease susceptibility. In this review, we discuss recent studies focusing on neural cells differentiated from SCZ and ASD patient iPSCs. These studies support a central role for glutamatergic synapse formation and function in both disorders and demonstrate that iPSC derived neurons offer a potential system for further evaluation of processes leading to synaptic dysregulation and for the design and screening of future therapies.
Keywords: Glutamatergic neurons; IPSCs; Neural development; Neurodevelopmental disorders; Synapses.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- DSM-5. 5th Edition Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC.
-
- Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, Garreta E, Consiglio A, Gonzalez F, Vassena R, Bilic J, Pekarik V, Tiscornia G, Edel M, Boue S, Izpisua Belmonte JC, 2008. Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat. Biotechnol 26, 1276–1284. - PubMed
-
- Ameis SH, Catani M, 2015. Altered white matter connectivity as a neural substrate for social impairment in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cortex 62, 158–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

