Mucosal IgG Levels Correlate Better with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Load and Inflammation than Plasma IgG Levels
- PMID: 26656116
- PMCID: PMC4783421
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00590-15
Mucosal IgG Levels Correlate Better with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Load and Inflammation than Plasma IgG Levels
Abstract
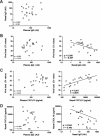
Maternal vaccination is currently considered a strategy against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections. In RSV-infected infants, high mucosal IgG levels correlated better with reduced RSV load and lower mucosal CXCL10 levels than plasma IgG levels. For future vaccination strategies against RSV, more focus should be on the mucosal humoral immune response.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Progress toward a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016 Jan 27;23(3):186-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00037-16. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26818954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reference deleted.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

