Genetic Mapping of Resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in Arachis stenosperma: A New Source of Nematode Resistance for Peanut
- PMID: 26656152
- PMCID: PMC4751557
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.115.023044
Genetic Mapping of Resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in Arachis stenosperma: A New Source of Nematode Resistance for Peanut
Abstract
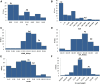
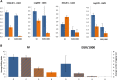
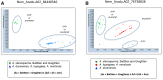
Root-knot nematodes (RKN; Meloidogyne sp.) are a major threat to crops in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. The use of resistant crop varieties is the preferred method of control because nematicides are expensive, and hazardous to humans and the environment. Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) is infected by four species of RKN, the most damaging being M. arenaria, and commercial cultivars rely on a single source of resistance. In this study, we genetically characterize RKN resistance of the wild Arachis species A. stenosperma using a population of 93 recombinant inbred lines developed from a cross between A. duranensis and A. stenosperma. Four quantitative trait loci (QTL) located on linkage groups 02, 04, and 09 strongly influenced nematode root galling and egg production. Drought-related, domestication and agronomically relevant traits were also evaluated, revealing several QTL. Using the newly available Arachis genome sequence, easy-to-use KASP (kompetitive allele specific PCR) markers linked to the newly identified RKN resistance loci were developed and validated in a tetraploid context. Therefore, we consider that A. stenosperma has high potential as a new source of RKN resistance in peanut breeding programs.
Keywords: Arachis; QTL; drought; introgression; marker-assisted selection; peanut; root-knot nematode resistance; yield.
Copyright © 2016 Leal-Bertioli et al.
Figures



References
-
- Bridge J., Page S. L. J., 1980. Estimation of root-knot nematode infestation levels on roots using a rating chart. Trop. Pest Manage. 26: 296–298.
-
- Caillaud M. C., Dubreuil G., Quentin M., Perfus-Barbeoch L., Lecomte P., et al. , 2008. Root-knot nematodes manipulate plant cell functions during a compatible interaction. J. Plant Physiol. 165(1): 104–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
