Quantum secured gigabit optical access networks
- PMID: 26656307
- PMCID: PMC4677342
- DOI: 10.1038/srep18121
Quantum secured gigabit optical access networks
Abstract
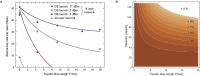
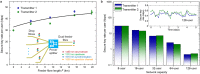
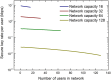
Optical access networks connect multiple endpoints to a common network node via shared fibre infrastructure. They will play a vital role to scale up the number of users in quantum key distribution (QKD) networks. However, the presence of power splitters in the commonly used passive network architecture makes successful transmission of weak quantum signals challenging. This is especially true if QKD and data signals are multiplexed in the passive network. The splitter introduces an imbalance between quantum signal and Raman noise, which can prevent the recovery of the quantum signal completely. Here we introduce a method to overcome this limitation and demonstrate coexistence of multi-user QKD and full power data traffic from a gigabit passive optical network (GPON) for the first time. The dual feeder implementation is compatible with standard GPON architectures and can support up to 128 users, highlighting that quantum protected GPON networks could be commonplace in the future.
Figures


References
-
- Lütkenhaus N. & Shields A. J. Focus on quantum cryptography: theory and practice. New J. Phys. 11, 045005 (2009).
-
- Scarani V. et al. The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301–1350 (2009).
-
- Korzh B. et al. Provable secure and practical quantum key distribution over 307 km of optical fibre. Nat. Photonics 9, 163 (2015).
-
- Shibata H., Honjo T. & Shimizu K. Quantum key distribution over a 72 dB channel loss using ultralow dark count superconducting single-photon detectors. Opt. Lett. 39, 5078–5081 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Elliott C. et al. Current status of the DARPA quantum network. In Donkor E. J., Pirich A. R. & Brandt H. E. (eds.) Quantum Information and Computation III (Proc. SPIE vol 5815), 138–149 (2005).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

