Oral Administration of 4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxycinnamaldehyde Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis by Inhibiting T Cell and Keratinocyte Activation
- PMID: 26656486
- PMCID: PMC4675532
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144521
Oral Administration of 4-Hydroxy-3-Methoxycinnamaldehyde Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis by Inhibiting T Cell and Keratinocyte Activation
Abstract
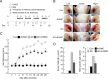
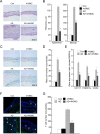
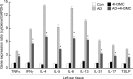
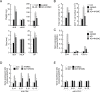
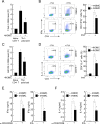
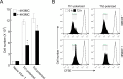
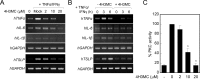
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a skin condition caused by an imbalance of distinct subsets of T helper cells. Previously, we showed that 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamaldehyde (4H3MC) inhibits T cell activation but does not induce apoptosis. Here, we examined the mechanism underlying the inhibitory effect of 4H3MC on AD both in vivo and in vitro. We sought to test the pharmacological effects of 4H3MC using a mouse model of 2, 4-'2,4-dinitrocholorobenzene' (DNCB)- and mite-induced AD. Also, we determined whether 4H3MC affects T cell differentiation and proliferation. Oral administration of 4H3MC attenuated the symptoms of DNCB- and mite-induced AD, including increased ear thickness, serum IgE levels, immune cell infiltration into inflammatory lesions, and pathogenic cytokine expression in ear tissues. In vitro, 4H3MC blocked T cell differentiation into Th1 and Th2 subtypes, as reflected by suppression of T-bet and GATA3, which are key transcription factors involved in T cell differentiation. In addition, 4H3MC downregulated T cell proliferation during Th1 and Th2 differentiation and keratinocyte activation. Collectively, these findings suggest that 4H3MC ameliorates AD symptoms by modulating the functions of effector T cells and keratinocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oleanolic acid acetate inhibits atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis in a murine model.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 May 15;269(1):72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23499868
-
Oral Administration of p-Hydroxycinnamic Acid Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis by Downregulating Th1 and Th2 Cytokine Production and Keratinocyte Activation.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 9;11(3):e0150952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150952. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26959360 Free PMC article.
-
Chrysin attenuates atopic dermatitis by suppressing inflammation of keratinocytes.Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Dec;110:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.10.025. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 29050978
-
The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Apr;139(4S):S65-S76. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.011. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28390479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory effects of selenium and strontium salts on keratinocyte-derived inflammatory cytokines.Arch Dermatol Res. 1995;287(7):680-2. doi: 10.1007/BF00371742. Arch Dermatol Res. 1995. PMID: 8534133 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Callicarpa dichotoma Leaf Extract Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis through the Suppression of T Cells and Keratinocytes Activation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;15(10):1280. doi: 10.3390/ph15101280. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297392 Free PMC article.
-
Water Extract of Rubus coreanus Prevents Inflammatory Skin Diseases In Vitro Models.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jun 17;10(6):1230. doi: 10.3390/plants10061230. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204204 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenol containing Sargassum horneri attenuated Th2 differentiation in splenocytes of ovalbumin-sensitised mice: involvement of the transcription factors GATA3/STAT5/NLRP3 in Th2 polarization.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):1464-1472. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1992451. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34726583 Free PMC article.
-
Allergy Inhibition Using Naturally Occurring Compounds Targeting Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Pathways: a Comprehensive Review.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2025 Mar 1;33(2):249-267. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.177. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 39933953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Administration of Liquiritigenin Confers Protection from Atopic Dermatitis through the Inhibition of T Cell Activation.Biomolecules. 2020 May 19;10(5):786. doi: 10.3390/biom10050786. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32438694 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

