Tumor Invasiveness, Not Lymphangiogenesis, Is Correlated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Unfavorable Prognosis in Young Breast Cancer Patients (≤35 Years)
- PMID: 26656588
- PMCID: PMC4676633
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144376
Tumor Invasiveness, Not Lymphangiogenesis, Is Correlated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Unfavorable Prognosis in Young Breast Cancer Patients (≤35 Years)
Abstract
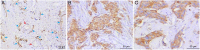
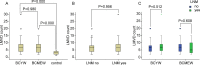
The morbidity rate of breast cancer is on the rise, and the age of onset appears to be trending toward a young age. Breast cancer in young women (BCYW) has a number of distinctive features that differ from breast cancer in middle-aged or elderly women (BCMEW). Lymphatic metastasis plays an important role in the spread of BCYW; however, the mechanisms of lymph node metastasis (LNM) in BCYW are not clear. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism of lymphatic metastasis in BCYW and to evaluate the relationships between lymphangiogenesis, the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) expression, clinicopathological characteristics, and prognosis. Using immunohistochemistry, MMP-9, VEGF-C and the level of lymphatic microvessel density (LMVD) were analyzed in 106 cases of breast invasive ductal carcinoma and 20 cases of breast proliferative lesions. Compared with BCMEW, BCYW had higher MMP-9 expression, higher LNM, and more adverse prognoses. In BCYW, high MMP-9 expression was positively correlated with LNM and impaired survival time. However, in BCMEW, MMP-9 expression was not correlated with LNM or survival time. In addition, high VEGF-C expression was positively correlated with a high level of LMVD in both BCYW and BCMEW. Nevertheless, a high level of LMVD was not correlated with LNM or survival time in the two groups. More importantly, univariate and multivariate survival analysis showed that MMP-9 expression and LNM were independent prognostic factors in BCYW. Our present study indicates that lymphangiogenesis induced by VEGF-C is augmented in breast cancer; however, a higher level of lymphangiogenesis has no significant impact on LNM or survival time. We suggest that tumor invasiveness, rather than lymphangiogenesis, plays an important role in LNM among BCYW. Moreover, MMP-9 and LNM were independent prognostic factors for BCYW.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
COX-2 expression is correlated with VEGF-C, lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in human cervical cancer.Microvasc Res. 2011 Sep;82(2):131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2011.04.011. Epub 2011 May 4. Microvasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21600223
-
[Role of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and -9 and vascular endothelial growth factor C in lymph node metastasis of breast cancer].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Apr;39(4):240-4. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20654122 Chinese.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha correlates with VEGF-C expression and lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006 Sep;99(2):135-41. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9190-3. Epub 2006 Mar 23. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006. PMID: 16555123
-
The non-canonical role of vascular endothelial growth factor-C axis in cancer progression.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Jun;240(6):718-24. doi: 10.1177/1535370215583802. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25888649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: Hermes between cancers and lymph nodes.Cancer Lett. 2025 Jul 28;623:217735. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217735. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 40268131 Review.
Cited by
-
High lymphatic vessel density and presence of lymphovascular invasion both predict poor prognosis in breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2017 May 17;17(1):335. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3338-x. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28514957 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-Embedded ShRNAs for Radiation-Inducible LGMN Knockdown and the Antitumor Effects on Breast Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 22;11(9):e0163446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163446. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27656894 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of MMP-9 and VEGF-C expression in North Indian women with breast cancer diagnosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Jul;457(1-2):93-103. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03515-w. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30993496 Clinical Trial.
-
The relationship of lymphatic vessel density, lymphovascular invasion, and lymph node metastasis in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):2863-2873. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13752. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27926511 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphovascular invasion is an independent predictor of survival in breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jun;157(3):555-64. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3837-5. Epub 2016 May 25. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27225388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson DG, Prevo R, Clasper S, Banerji S. LYVE-1, the lymphatic system and tumor lymphangiogenesis. Trends in immunology. 2001;22(6):317–321. - PubMed
-
- Zhuo W, Jia L, Song N, Lu XA, Ding Y, Wang X, et al. The CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine pathway: a novel axis regulates lymphangiogenesis. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2012;18(19):5387–5398. - PubMed
-
- Gnerlich JL, Deshpande AD, Jeffe DB, Sweet A, White N, Margenthaler JA. Elevated breast cancer mortality in women younger than age 40 years compared with older women is attributed to poorer survival in early-stage disease. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 2009;208(3):341–347. 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2008.12.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

