TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 26656660
- PMCID: PMC4809675
- DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.169
TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies
Abstract
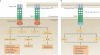
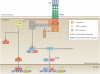
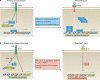
TNF is a pleiotropic cytokine with important functions in homeostasis and disease pathogenesis. Recent discoveries have provided insights into TNF biology that introduce new concepts for the development of therapeutics for TNF-mediated diseases. The model of TNF receptor signalling has been extended to include linear ubiquitination and the formation of distinct signalling complexes that are linked with different functional outcomes, such as inflammation, apoptosis and necroptosis. Our understanding of TNF-induced gene expression has been enriched by the discovery of epigenetic mechanisms and concepts related to cellular priming, tolerization and induction of 'short-term transcriptional memory'. Identification of distinct homeostatic or pathogenic TNF-induced signalling pathways has introduced the concept of selectively inhibiting the deleterious effects of TNF while preserving its homeostatic bioactivities for therapeutic purposes. In this Review, we present molecular mechanisms underlying the roles of TNF in homeostasis and inflammatory disease pathogenesis, and discuss novel strategies to advance therapeutic paradigms for the treatment of TNF-mediated diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Feldmann M. Translating molecular insights in autoimmunity into effective therapy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009;27:1–27. - PubMed
-
- Cerami A. The value of failure: the discovery of TNF and its natural inhibitor erythropoietin. J. Intern. Med. 2011;269:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Lee RA, Eisen DB. Treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa with biologic medications. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015;73:S82–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

