A pH Sensitive High-Throughput Assay for miRNA Binding of a Peptide-Aminoglycoside (PA) Library
- PMID: 26656788
- PMCID: PMC4699463
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144251
A pH Sensitive High-Throughput Assay for miRNA Binding of a Peptide-Aminoglycoside (PA) Library
Abstract
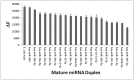
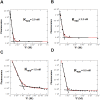
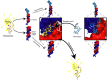
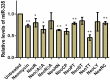
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are small RNAs that have a regulatory role in gene expression. Because of this regulatory role, miRNAs have become a new target for therapeutic compounds. Here, we outline an approach to target specific miRNAs using a high throughput capable assay and a 215 compound peptidic-aminosugar (PA) library. Aminosugars have been shown in a number of recent reports as important lead compounds that bind miRNA. In order to screen for compounds that bind miRNA, we have developed a high throughput displacement assay using a fluorescein-neomycin conjugated molecule (F-neo) as a probe for competitive miRNA binding compounds. We have applied the F-neo assay to four different miRNA constructs and the assay is applicable to most miRNAs, at various stages of processing. The results of the screen were validated by the determination of the IC50 for a select group of compounds from the library. For example, we identified eight compounds that bind to hsa-miR 504 with higher affinity than the parent neomycin. From the F-neo displacement assay we found that the number of binding sites differs for each miRNA, and the binding sites appear to differ both physically and chemically, with different affinity of the compounds resulting from the size of the molecule as well as the chemical structure. Additionally, the affinity of the compounds was dependent on the identity and position of the amino acid position of conjugation and the affinity of the compounds relative to other compounds in the library was miRNA dependent with the introduction of a second amino acid.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
Pre-microRNA binding aminoglycosides and antitumor drugs as inhibitors of Dicer catalyzed microRNA processing.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Feb 15;22(4):1709-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.12.103. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22257890
-
A fluorescent aminosugar to rapidly screen and study RNA binders.Methods Enzymol. 2019;623:291-314. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2019.05.027. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Methods Enzymol. 2019. PMID: 31239051
-
A molecular-beacon-based screen for small molecule inhibitors of miRNA maturation.ACS Chem Biol. 2013 May 17;8(5):930-8. doi: 10.1021/cb300650y. Epub 2013 Mar 6. ACS Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23402670
-
Thermodynamics of aminoglycoside-rRNA recognition.Biopolymers. 2003 Sep;70(1):58-79. doi: 10.1002/bip.10411. Biopolymers. 2003. PMID: 12925993 Review.
-
Fluorescence-based methods for evaluating the RNA affinity and specificity of HIV-1 Rev-RRE inhibitors.Biopolymers. 2003 Sep;70(1):103-19. doi: 10.1002/bip.10428. Biopolymers. 2003. PMID: 12925996 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential for the Development of a New Generation of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics.Pharm Chem J. 2021;55(9):860-875. doi: 10.1007/s11094-021-02510-0. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Pharm Chem J. 2021. PMID: 35039693 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA inhibition by proximity-enabled Dicer inactivation.Methods. 2019 Sep 1;167:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 9. Methods. 2019. PMID: 31077820 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic action between peptide-neomycin conjugates and polymyxin B against multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2025 Aug 7;16:1605813. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1605813. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40851856 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent indicator displacement assays to identify and characterize small molecule interactions with RNA.Methods. 2019 Sep 1;167:3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.04.018. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Methods. 2019. PMID: 31051253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arginine-linked neomycin B dimers: synthesis, rRNA binding, and resistance enzyme activity.Medchemcomm. 2016 Jan 1;7(1):164-169. doi: 10.1039/C5MD00427F. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Medchemcomm. 2016. PMID: 26811742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004. January 23;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993. December 3;75(5):843–854. - PubMed
-
- Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993. December 3;75(5):855–862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

