The Global Health Impact Index: Promoting Global Health
- PMID: 26657064
- PMCID: PMC4676606
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141374
The Global Health Impact Index: Promoting Global Health
Erratum in
-
Correction: The Global Health Impact Index: Promoting Global Health.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 5;11(2):e0148946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148946. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26849444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Millions of people cannot access essential medicines they need for deadly diseases like malaria, tuberculosis (TB) and HIV/AIDS. There is good information on the need for drugs for these diseases but until now, no global estimate of the impact drugs are having on this burden. This paper presents a model measuring companies' key malaria, TB and HIV/AIDS drugs' consequences for global health (global-health-impact.org). It aggregates drugs' impacts in several ways-by disease, country and originator-company. The methodology can be extended across diseases as well as drugs to provide a more extensive picture of the impact companies' drugs are having on the global burden of disease. The study suggests that key malaria, TB and HIV/AIDS drugs are, together, ameliorating about 37% of the global burden of these diseases and Sanofi, Novartis, and Pfizer's drugs are having the largest effect on this burden. Moreover, drug impacts vary widely across countries. This index provides important information for policy makers, pharmaceutical companies, countries, and other stake-holders that can help increase access to essential medicines.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
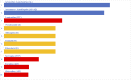
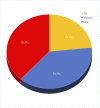
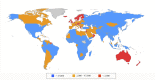
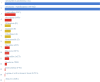
Similar articles
-
Hopes that Novartis deal on tuberculosis will spur donations for HIV and malaria.BMJ. 2004 Jan 10;328(7431):70. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7431.70-a. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 14715592 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pilot assessment of supply chains for pharmaceuticals and medical commodities for malaria, tuberculosis and HIV infection in Ethiopia.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2012 Jan;106(1):60-2. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2011.09.008. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2012. PMID: 22093812
-
The danger of in-kind drug donations to the Global Fund.Lancet. 2009 Apr 4;373(9670):1218-21. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61487-7. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Lancet. 2009. PMID: 18848353 Review. No abstract available.
-
Ensuring access to essential medicines: some economic considerations.Spec Law Dig Health Care Law. 2003 Jul;(291):9-25. Spec Law Dig Health Care Law. 2003. PMID: 15206162 No abstract available.
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Correction: The Global Health Impact Index: Promoting Global Health.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 5;11(2):e0148946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148946. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26849444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2011/12 tuberculosis global facts Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012. Available: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/2011/factsheet_tb_2011.pdf. Accessed 25 Oct 2015.
-
- World Health Organization. Key facts on global HIV epidemic and progress in 2010 Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011. Available: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/progress_report2011/global_facts/en/. Accessed 25 Oct 2015.
-
- World Health Organization. World malaria report 2011 fact sheet. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011. Available: http://www.who.int/malaria/world_malaria_report_2011/WMR2011_factsheet.pdf. Accessed 25 Oct 2015.
-
- World Bank. How we classify countries Washington: World Bank; Available: http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-classifications. Accessed 5 Jan 5 2013.
-
- de Francisco A, Stephen M, editors. Monitoring financial flows for health research 2006: the changing landscape of health research for development Geneva: Global Forum for Health Research; 2006. Available: http://www.isn.ethz.ch/Digital-Library/Publications/Detail/?ots591=0c54e.... Accessed 4 Feb 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

