Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of site-specific isotopically labeled nucleotides for use in NMR resonance assignment, dynamics and structural characterizations
- PMID: 26657632
- PMCID: PMC4824079
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1333
Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of site-specific isotopically labeled nucleotides for use in NMR resonance assignment, dynamics and structural characterizations
Abstract
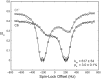
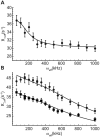
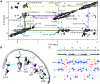
Stable isotope labeling is central to NMR studies of nucleic acids. Development of methods that incorporate labels at specific atomic positions within each nucleotide promises to expand the size range of RNAs that can be studied by NMR. Using recombinantly expressed enzymes and chemically synthesized ribose and nucleobase, we have developed an inexpensive, rapid chemo-enzymatic method to label ATP and GTP site specifically and in high yields of up to 90%. We incorporated these nucleotides into RNAs with sizes ranging from 27 to 59 nucleotides using in vitro transcription: A-Site (27 nt), the iron responsive elements (29 nt), a fluoride riboswitch from Bacillus anthracis(48 nt), and a frame-shifting element from a human corona virus (59 nt). Finally, we showcase the improvement in spectral quality arising from reduced crowding and narrowed linewidths, and accurate analysis of NMR relaxation dispersion (CPMG) and TROSY-based CEST experiments to measure μs-ms time scale motions, and an improved NOESY strategy for resonance assignment. Applications of this selective labeling technology promises to reduce difficulties associated with chemical shift overlap and rapid signal decay that have made it challenging to study the structure and dynamics of large RNAs beyond the 50 nt median size found in the PDB.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

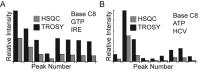
Similar articles
-
Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of selectively ¹³C/¹⁵N-labeled RNA for NMR structural and dynamics studies.Methods Enzymol. 2014;549:133-62. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-801122-5.00007-6. Methods Enzymol. 2014. PMID: 25432748 Free PMC article.
-
Regio-selective chemical-enzymatic synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides facilitates RNA structure and dynamics studies.Chembiochem. 2014 Jul 21;15(11):1573-7. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201402130. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Chembiochem. 2014. PMID: 24954297 Free PMC article.
-
Noncovalent spin labeling of riboswitch RNAs to obtain long-range structural NMR restraints.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Jun 20;9(6):1330-9. doi: 10.1021/cb500050t. Epub 2014 Apr 10. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24673892
-
Chemo-enzymatic labeling for rapid assignment of RNA molecules.Methods. 2016 Jul 1;103:11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.03.015. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Methods. 2016. PMID: 27090003 Review.
-
Stable isotope labeling methods for DNA.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2016 Aug;96:89-108. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2016. PMID: 27573183 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective [9-15N] Guanosine for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Large Ribonucleic Acids.Chembiochem. 2025 Jun 16;26(12):e202500206. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202500206. Epub 2025 May 23. Chembiochem. 2025. PMID: 40320375 Free PMC article.
-
NMR characterization of RNA small molecule interactions.Methods. 2019 Sep 1;167:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.05.015. Epub 2019 May 22. Methods. 2019. PMID: 31128236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Dynamics by NMR Spectroscopy.Chembiochem. 2019 Nov 4;20(21):2685-2710. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201900072. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Chembiochem. 2019. PMID: 30997719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCR5 RNA Pseudoknots: Residue and Site-Specific Labeling correlate Internal Motions with microRNA Binding.Chemistry. 2018 Apr 11;24(21):5462-5468. doi: 10.1002/chem.201705948. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Chemistry. 2018. PMID: 29412477 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing micro-to-millisecond chemical exchange in nucleic acids using off-resonance R1ρ relaxation dispersion.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2019 Jun-Aug;112-113:55-102. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 11. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2019. PMID: 31481159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Winkler W., Nahvi A., Breaker R.R. Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. Nature. 2002;419:952–956. - PubMed
-
- Reining A., Nozinovic S., Schlepckow K., Buhr F., Fürtig B., Schwalbe H. Three-state mechanism couples ligand and temperature sensing in riboswitches. Nature. 2013;499:355–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

