Presynaptic hyperpolarization induces a fast analogue modulation of spike-evoked transmission mediated by axonal sodium channels
- PMID: 26657943
- PMCID: PMC4682119
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10163
Presynaptic hyperpolarization induces a fast analogue modulation of spike-evoked transmission mediated by axonal sodium channels
Abstract
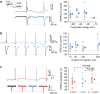
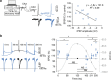
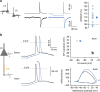
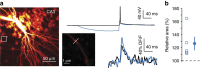
In the mammalian brain, synaptic transmission usually depends on presynaptic action potentials (APs) in an all-or-none (or digital) manner. Recent studies suggest, however, that subthreshold depolarization in the presynaptic cell facilitates spike-evoked transmission, thus creating an analogue modulation of a digital process (or analogue-digital (AD) modulation). At most synapses, this process is slow and not ideally suited for the fast dynamics of neural networks. We show here that transmission at CA3-CA3 and L5-L5 synapses can be enhanced by brief presynaptic hyperpolarization such as an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP). Using dual soma-axon patch recordings and live imaging, we find that this hyperpolarization-induced AD facilitation (h-ADF) is due to the recovery from inactivation of Nav channels controlling AP amplitude in the axon. Incorporated in a network model, h-ADF promotes both pyramidal cell synchrony and gamma oscillations. In conclusion, cortical excitatory synapses in local circuits display hyperpolarization-induced facilitation of spike-evoked synaptic transmission that promotes network synchrony.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analog modulation of spike-evoked transmission in CA3 circuits is determined by axonal Kv1.1 channels in a time-dependent manner.Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Feb;41(3):293-304. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12787. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Eur J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25394682
-
Effects of axonal topology on the somatic modulation of synaptic outputs.J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 22;32(8):2868-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5365-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22357869 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic membrane potential and Kv1 channels control spike repolarization in cortical axon collaterals and presynaptic boutons.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 26;31(43):15490-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2752-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22031895 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal signaling in central nervous system.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011 Feb 25;63(1):1-8. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21340428 Review.
-
Backpropagation of action potentials generated at ectopic axonal loci: hypothesis that axon terminals integrate local environmental signals.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1995 Jul;21(1):42-92. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(95)00004-m. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1995. PMID: 8547954 Review.
Cited by
-
Technologies to Study Action Potential Propagation With a Focus on HD-MEAs.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Apr 26;13:159. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00159. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31118887 Free PMC article.
-
The computational power of the human brain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Aug 7;17:1220030. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1220030. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37608987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Axonal Na+ channels detect and transmit levels of input synchrony in local brain circuits.Sci Adv. 2020 May 6;6(19):eaay4313. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay4313. eCollection 2020 May. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32494697 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Control of Neurotransmitter Release by Presynaptic Potential.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Dec 5;10:278. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00278. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27994539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analogue modulation of back-propagating action potentials enables dendritic hybrid signalling.Nat Commun. 2016 Oct 5;7:13033. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13033. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27703164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimahara T. & Peretz B. Soma potential of an interneurone controls transmitter release in a monosynaptic pathway in Aplysia. Nature 273, 158–160 (1978) . - PubMed
-
- Shu Y., Hasenstaub A., Duque A., Yu Y. & McCormick D. A. Modulation of intracortical synaptic potentials by presynaptic somatic membrane potential. Nature 441, 761–765 (2006) . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

