Emerging therapeutic drugs for AML
- PMID: 26660428
- PMCID: PMC4915807
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-604538
Emerging therapeutic drugs for AML
Abstract
Multiple new drugs are being developed to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), including novel formulations of traditional chemotherapy-antibody drug conjugates and agents that target specific mutant enzymes. Next-generation sequencing has allowed us to discover the genetic mutations that lead to the development and clinical progression of AML. Studies of clonal hierarchy suggest which mutations occur early and dominate. This has led to targeted therapy against mutant driver proteins as well as the development of drugs such as CPX-351 and SGN-CD33A whose mechanisms of action and efficacy may not be dependent on mutational complexity. In this brief review, we discuss drugs that may emerge as important for the treatment of AML in the next 10 years.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01696084.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


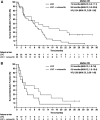
References
-
- Burnett A, Wetzler M, Löwenberg B. Therapeutic advances in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(5):487–494. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield CD, Lawrence D, Byrd JC, et al. Frequency of prolonged remission duration after high-dose cytarabine intensification in acute myeloid leukemia varies by cytogenetic subtype. Cancer Res. 1998;58(18):4173–4179. - PubMed
-
- Rowe JM. Important milestones in acute leukemia in 2013. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2013;26(3):241–244. - PubMed
-
- Appelbaum FR, Kopecky KJ, Tallman MS, et al. The clinical spectrum of adult acute myeloid leukaemia associated with core binding factor translocations. Br J Haematol. 2006;135(2):165–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

