Treatment of tibia avulsion fracture of posterior cruciate ligament with high-strength suture fixation under arthroscopy
- PMID: 26660676
- PMCID: PMC5306319
- DOI: 10.1007/s00068-015-0606-9
Treatment of tibia avulsion fracture of posterior cruciate ligament with high-strength suture fixation under arthroscopy
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the outcome of arthroscopy treatment using high-strength line in the treatment of tibial avulsion fracture of posterior cruciate ligament.
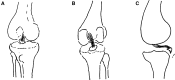
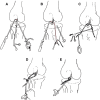
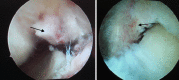
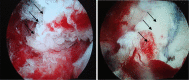
Methods: Both the avulsed bone block and the tibia bone bed were refreshed. The procedure was completed with the assistance of PCL director drill guide. The reduction and fixation using high-strength line were used to fix the avulsed bone by from posterior middle portal. Rehabilitation began early postoperatively.
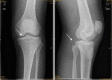
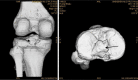
Results: From January 2010 to June 2012, a total of 18 arthroscopically treated cases of PCL tibial avulsion fracture were retrospectively evaluated. Reduction of the avulsion fragment was obtained in all cases. 16 cases were followed up for 7-30 months (average 13.6), and 2 cases were out of follow-up. In the 16 followed patients, flexion and extension were back to normal within 6 weeks, and return to normal walk in 12 weeks. The bone healing was good without any vascular or nerve complications. All the patients regained the preinjury activity level. The mean score (and standard deviation) increased from 38.9 ± 4.9 points to 95.2 ± 3.8 points with the system of Lysholm, from 57.1 ± 10.3 points to 94.3 ± 4.4 points with the system of IKDC. Post-test displacement of KT3000 declined from 3.6 ± 0.39 to 1.1 ± 0.27 mm.
Conclusion: Arthroscopic vertical fixation by high-strength line is a simple, safe, reliable, and micro-invasive treatment to PCL tibial avulsion fracture. It is a kind of real all arthroscopic technique, and good for early postoperative rehabilitation. The total stability of the knee could be gained, and the second operation to remove the internal fixation is avoided.
Keywords: Arthroscopy; Avulsion fracture; High-strength line; Posterior cruciate ligament.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards Each subject had signed the informed consent before participating in our study. This study was approved by the ethics committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University and was conducted in conformity with the guidelines outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki statement. Conflict of interest Weimin Zhu, Wei Lu, Jiaming Cui, Liangquan Peng, kan OuYang, Hao Li, Haifeng Liu, Wei You, Daping Wang, and Yanjun Zeng declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chen CW, Chen L, Pan ZE, Yang SW. Open reduction and internal fixation via a posterior approach for posterior fractures of tibial plateau. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(7):561–565. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

