Mucosal Barrier Depletion and Loss of Bacterial Diversity are Primary Abnormalities in Paediatric Ulcerative Colitis
- PMID: 26660940
- PMCID: PMC4946763
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv223
Mucosal Barrier Depletion and Loss of Bacterial Diversity are Primary Abnormalities in Paediatric Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
Background and aims: Ulcerative colitis [UC] is associated with colonic mucosa barrier defects and bacterial dysbiosis, but these features may simply be the result of inflammation. Therefore, we sought to assess whether these features are inherently abrogated in the terminal ileum [TI] of UC patients, where inflammation is absent.
Methods: TI biopsies from paediatric inflammatory bowel disease [IBD] subsets [Crohn's disease [CD; n = 13] and UC [n = 10]], and non-IBD disease controls [n = 12] were histologically graded, and alcian blue/periodic acid-Schiff stained biopsies were quantified. The mucosal barrier was assessed for mucin [MUC2], immunoglobulin [Ig]A, IgG, and total bacteria (fluorescence in-situ hybridisation [FISH probe EUB338]) by immunofluorescence. The regulation of mucin secretion was investigated by NLRP6 gene expression and immunofluorescence. The composition of the active mucosa-associated microbiota was explored by sequencing the 16S rRNA amplicon generated from total RNA.
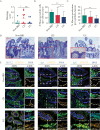
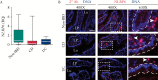
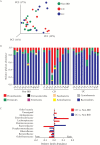
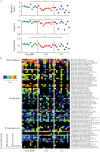
Results: Despite the absence of ileitis, UC patients displayed ileal barrier depletion illustrated by reductions in mucin-containing goblet cells and mucin production and altered epithelial NLRP6 expression. In both CD patients with ileitis and UC patients with normal histology, bacteria coated with IgA and IgG penetrated the TI mucin layer. Biopsy 16S rRNA sequencing revealed a reduction in α-diversity by three methods [Shannon, Simpson, and Equitability indices] between UC and non-IBD paediatric patients.
Conclusions: These findings suggest an underlying defect in the UC-afflicted intestinal tract even in the absence of inflammation, implicating barrier and microbial changes as primary abnormalities in UC that may play a causative role in disease development.
Keywords: Ulcerative colitis; mucin; mucosal barrier.
Copyright © 2015 European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- El Aidy S, Merrifield CA, Derrien M, et al. The gut microbiota elicits a profound metabolic reorientation in the mouse jejunal mucosa during conventionalisation. Gut 2013;62:1306–14. - PubMed
-
- Sanchez de Medina F, Romero-Calvo I, Mascaraque C, Martinez-Augustin O. Intestinal inflammation and mucosal barrier function. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014;20:2394–404. - PubMed
-
- Johansson ME. Mucus layers in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014;20:2124–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

