Cerebral small vessel disease: Capillary pathways to stroke and cognitive decline
- PMID: 26661176
- PMCID: PMC4759673
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X15606723
Cerebral small vessel disease: Capillary pathways to stroke and cognitive decline
Abstract
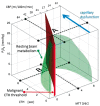
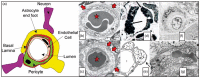
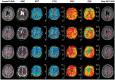
Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) gives rise to one in five strokes worldwide and constitutes a major source of cognitive decline in the elderly. SVD is known to occur in relation to hypertension, diabetes, smoking, radiation therapy and in a range of inherited and genetic disorders, autoimmune disorders, connective tissue disorders, and infections. Until recently, changes in capillary patency and blood viscosity have received little attention in the aetiopathogenesis of SVD and the high risk of subsequent stroke and cognitive decline. Capillary flow patterns were, however, recently shown to limit the extraction efficacy of oxygen in tissue and capillary dysfunction therefore proposed as a source of stroke-like symptoms and neurodegeneration, even in the absence of physical flow-limiting vascular pathology. In this review, we examine whether capillary flow disturbances may be a shared feature of conditions that represent risk factors for SVD. We then discuss aspects of capillary dysfunction that could be prevented or alleviated and therefore might be of general benefit to patients at risk of SVD, stroke or cognitive decline.
Keywords: Cerebral small vessel disease; capillary dysfunction; dementia; oxygenation; stroke.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Figures
References
-
- Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 2010; 9: 689–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

