Ectodermal Wnt controls nasal pit morphogenesis through modulation of the BMP/FGF/JNK signaling axis
- PMID: 26661618
- PMCID: PMC4774528
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.24376
Ectodermal Wnt controls nasal pit morphogenesis through modulation of the BMP/FGF/JNK signaling axis
Abstract
Background: Mutations of WNT3, WNT5A, WNT9B, and WNT11 genes are associated with orofacial birth defects, including nonsyndromic cleft lip with cleft palate in humans. However, the source of Wnt ligands and their signaling effects on the orofacial morphogenetic process remain elusive.
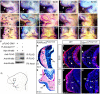
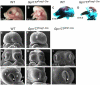
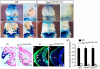
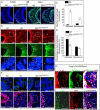
Results: Using Foxg1-Cre to impair Wnt secretion through the inactivation of Gpr177/mWls, we investigate the relevant regulation of Wnt production and signaling in nasal-facial development. Ectodermal ablation of Gpr177 leads to severe facial deformities resulting from dramatically reduced cell proliferation and increased cell death due to a combined loss of WNT, FGF and BMP signaling in the developing facial prominence. In the invaginating nasal pit, the Gpr177 disruption also causes a detrimental effect on migration of the olfactory epithelial cells into the mesenchymal region. The blockage of Wnt secretion apparently impairs the olfactory epithelial cells through modulation of JNK signaling.
Conclusions: Our study thus suggests the head ectoderm, including the facial ectoderm and the neuroectoderm, as the source of canonical as well as noncanonical Wnt ligands during early development of the nasal-facial prominence. Both β-catenin-dependent and -independent signaling pathways are required for proper development of these morphogenetic processes.
Keywords: Gpr177; JNK; Wntless; canonical Wnt; nasal pit; noncanonical Wnt.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gpr177-mediated Wnt Signaling Is Required for Secondary Palate Development.J Dent Res. 2015 Jul;94(7):961-7. doi: 10.1177/0022034515583532. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25922332
-
Specific induction of cranial placode cells from Xenopus ectoderm by modulating the levels of BMP, Wnt, and FGF signaling.Genesis. 2015 Oct;53(10):652-9. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22881. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Genesis. 2015. PMID: 26249012
-
The canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway regulates Fgf signaling for early facial development.Dev Biol. 2011 Jan 15;349(2):250-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.11.004. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21070765
-
Molecular signaling directing neural plate border formation.Int J Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 9;68(2):65-78. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.230231me. Int J Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39016374 Review.
-
Growth factor regulation of lens development.Dev Biol. 2005 Apr 1;280(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.01.020. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15766743 Review.
Cited by
-
Segmentation of Tissues and Proliferating Cells in Light-Sheet Microscopy Images of Mouse Embryos Using Convolutional Neural Networks.IEEE Access. 2022;10:105084-105100. doi: 10.1109/access.2022.3210542. Epub 2022 Sep 28. IEEE Access. 2022. PMID: 36660260 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models in palate development and orofacial cleft research: Understanding the crucial role and regulation of epithelial integrity in facial and palate morphogenesis.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2022;148:13-50. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2021.12.003. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35461563 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomic signatures and gene regulatory networks modulated by Wls in mammalian midline facial formation and clefts.Development. 2022 Jul 15;149(14):dev200533. doi: 10.1242/dev.200533. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Development. 2022. PMID: 35781558 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-layered mutation in hedgehog-related genes in Gorlin syndrome may affect the phenotype.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 15;12(9):e0184702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184702. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28915250 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-Bound GeneSwitch Causes Developmental Aberrations in Drosophila that Are Alleviated by the Alternative Oxidase.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Sep 8;6(9):2839-46. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.030882. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27412986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahtiainen L, Lefebvre S, Lindfors PH, Renvoise E, Shirokova V, Vartiainen MK, Thesleff I, Mikkola ML. Directional cell migration, but not proliferation, drives hair placode morphogenesis. Dev Cell. 2014;28:588–602. - PubMed
-
- Al Alam D, Green M, Tabatabai Irani R, Parsa S, Danopoulos S, Sala FG, Branch J, El Agha E, Tiozzo C, Voswinckel R, Jesudason EC, Warburton D, Bellusci S. Contrasting expression of canonical Wnt signaling reporters TOPGAL, BATGAL and Axin2(LacZ) during murine lung development and repair. PLoS One. 2011;6:e23139. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachler M, Neubuser A. Expression of members of the Fgf family and their receptors during midfacial development. Mech Dev. 2001;100:313–316. - PubMed
-
- Banziger C, Soldini D, Schutt C, Zipperlen P, Hausmann G, Basler K. Wntless, a conserved membrane protein dedicated to the secretion of Wnt proteins from signaling cells. Cell. 2006;125:509–522. - PubMed
-
- Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Gregorieff A, Leucht P, ten Berge D, Fuerer C, Clevers H, Nusse R, Helms JA. Wnt signaling mediates regional specification in the vertebrate face. Development. 2007;134:3283–3295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

