Urethral (indwelling or intermittent) or suprapubic routes for short-term catheterisation in hospitalised adults
- PMID: 26661940
- PMCID: PMC8612698
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004203.pub3
Urethral (indwelling or intermittent) or suprapubic routes for short-term catheterisation in hospitalised adults
Abstract
Background: Indwelling urethral catheters are often used for bladder drainage in hospital. Urinary tract infection is the most common hospital-acquired infection, and a common complication of urinary catheterisation. Pain, ease of use and quality of life are important to consider, as well as formal economic analysis. Suprapubic catheterisation can also result in bowel perforation and death.
Objectives: To determine the advantages and disadvantages of alternative routes of short-term bladder catheterisation in adults in terms of infection, adverse events, replacement, duration of use, participant satisfaction and cost effectiveness. For the purpose of this review, we define 'short-term' as intended duration of catheterisation for 14 days or less.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Group Specialised Register, which contains trials identified from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, MEDLINE in process, ClinicalTrials.gov, WHO ICTRP and handsearching of journals and conference proceedings (searched 26 February 2015), CINAHL (searched 27 January 2015) and the reference lists of relevant articles.
Selection criteria: We included all randomised and quasi-randomised trials comparing different routes of catheterisation for short-term use in hospitalised adults.
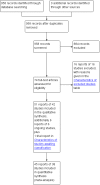
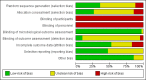
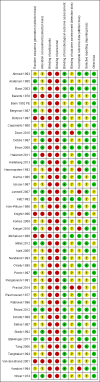
Data collection and analysis: At least two review authors extracted data and performed 'Risk of bias' assessment of the included trials. We sought clarification from the trialists if further information was required.
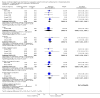
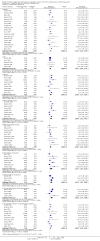
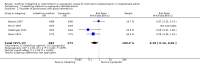
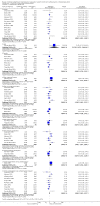
Main results: In this systematic review, we included 42 trials.Twenty-five trials compared indwelling urethral and suprapubic catheterisation. There was insufficient evidence for symptomatic urinary tract infection (risk ratio (RR) 1.01, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.61 to 1.69; 5 trials, 575 participants; very low-quality evidence). Participants with indwelling catheters had more cases of asymptomatic bacteriuria (RR 2.25, 95% CI 1.63 to 3.10; 19 trials, 1894 participants; very low quality evidence) and more participants reported pain (RR 5.62, 95% CI 3.31 to 9.55; 4 trials, 535 participants; low-quality evidence). Duration of catheterisation was shorter in the indwelling urethral catheter group (MD -1.73, 95% CI -2.42 to -1.05; 2 trials, 274 participants).Fourteen trials compared indwelling urethral catheterisation with intermittent catheterisation. Two trials had data for symptomatic UTI which were suitable for meta-analysis. Due to evidence of significant clinical and statistical heterogeneity, we did not pool the results, which were inconclusive and the quality of evidence was very low. The main source of heterogeneity was the reason for hospitalisation as Hakvoort and colleagues recruited participants undergoing urogenital surgery; whereas in the trial conducted by Tang and colleagues elderly women in geriatric rehabilitation ward were recruited. The evidence was also inconclusive for asymptomatic bacteriuria (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.85 to 1.28; 13 trials, 1333 participants; very low quality evidence). Almost three times as many people developed acute urinary retention with the intermittent catheter (16% with urethral versus 45% with intermittent); RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.91; 4 trials, 384 participants.Three trials compared intermittent catheterisation with suprapubic catheterisation, with only female participants. The evidence was inconclusive for symptomatic urinary tract infection, asymptomatic bacteriuria, pain or cost.None of the trials reported the following critical outcomes: quality of life; ease of use, and cost utility analysis.
Authors' conclusions: Suprapubic catheters reduced the number of participants with asymptomatic bacteriuria, recatheterisation and pain compared with indwelling urethral. The evidence for symptomatic urinary tract infection was inconclusive.For indwelling versus intermittent urethral catheterisation, the evidence was inconclusive for symptomatic urinary tract infection and asymptomatic bacteriuria. No trials reported pain.The evidence was inconclusive for suprapubic versus intermittent urethral catheterisation. Trials should use a standardised definition for symptomatic urinary tract infection. Further adequately-powered trials comparing all catheters are required, particularly suprapubic and intermittent urethral catheterisation.
Conflict of interest statement
Emily Kidd: none known Fiona Stewart: none known Nadine Kassis: none known Emily Hom: none known Muhammad Imran Omar: none known
Figures




































Update of
-
Urinary catheter policies for short-term bladder drainage in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD004203. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004203.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 10;(12):CD004203. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004203.pub3. PMID: 16034924 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ahmed 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ahmed MS. Urinary tract infection in relation to pre‐operative catheterization: suprapubic versus urethral catheters. Pakistan Journal of Surgery 1993;9(2):43‐8. [sr‐incont35911]
Andersen 1985 {published data only}
-
- Andersen JT, Heisterberg L, Hebjorn S, Petersen K, Stampe Sorensen S, Fischer‐Rasmussen W, et al. Suprapubic versus transurethral bladder drainage after colposuspension/vaginal repair. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1985;64(2):139‐43. [sr‐incont616] - PubMed
Baan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Baan AH, Vermeulen H, Meulen J, Bossuyt P, Olszyna D, Gouma DJ. The effect of suprapubic catheterization versus transurethral catheterization after abdominal surgery on urinary tract infection: a randomized controlled trial. Digestive Surgery 2003;20(4):290‐5. [sr‐incont23330] - PubMed
Barents 1978 {published data only}
-
- Barents JW, Dankert J, Ilic P, Laanbroek HJ, Vries H. The indwelling catheter in gynecology and the development of bacteriuria; a comparative study of patients with the transurethral and the suprapubic catheter. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde 1978;122(36):1321‐7. [sr‐incont7620] - PubMed
Barry 1992 PE {published data only}
-
- Barry M, Gillen P, McNicholas M, Travnor O, Hyland J. A prospective, randomized controlled trial of urethral vs. suprapubic bladder catheterisation in abdominal surgery (Abstract number 69). Irish Journal of Medical Science 1992;161(8):540. [18538]
Bergman 1987 {published data only}
-
- Bergman A, Matthews L, Ballard CA, Roy S. Suprapubic versus transurethral bladder drainage after surgery for stress urinary incontinence. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1987;69(4):546‐9. [sr‐incont551] - PubMed
Botsios 1997 {published data only}
-
- Botsios D, Demetriades C, Goulimaris I, Kanellos I, Dadoukis I. Suprapubic percutaneous cystostomy versus urethral catheterisation in abdominal surgery. A prospective randomised controlled study. Digestive Surgery 1997;14:404‐8. [sr‐incont6768]
Carpiniello 1988 {published data only}
-
- Carpiniello VL, Cendron M, Altman HG, Malloy TR, Booth R. Treatment of urinary complications after total joint replacement in elderly females. Urology 1988;32(3):186‐8. [sr‐incont1179] - PubMed
Dixon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Dixon L, Dolan M, Brown K, Hilton P. RCT of urethral versus suprapubic catheterization. British Journal of Nursing 2010;19(18):s7‐s13. [ISRCTN66645527; sr‐incont40340] - PubMed
-
- ISRCTN66645527. Intermittent urethral versus indwelling suprapubic catheterisation in the management of voiding after urogynaecological surgery: a randomised single centre controlled trial. isrctn.org/ISRCTN66645527 (accessed 12th November 2015). [ISRCTN66645527; sr‐incont64580]
Dobbs 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dobbs SP, Jackson SR, Wilson AM, Maplethorpe RP, Hammond RH. A prospective, randomized trial comparing continuous bladder drainage with catheterization at abdominal hysterectomy. British Journal of Urology 1997;80(4):554‐6. [sr‐incont6720] - PubMed
Evron 2008 {published data only}
-
- Evron S, Dimitrochenko V, Khazin V, Sherman A, Sadan O, Boaz M, et al. The effect of intermittent versus continuous bladder catheterization on labor duration and postpartum urinary retention and infection: a randomized trial. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2008;20(8):567‐72. [sr‐incont31242] - PubMed
-
- Rigini N, Evron S, Sadan O, Szmuk P, Ezri T. Intermittent versus continuous bladder catheterization and labor epidural (Abstract). Anesthesiology 2006;105:A907. [23732]
Hakvoort 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hakvoort RA, Thijs S, Bouwmeester F, Ruhe I, Vernooil M, Broekman A, et al. Optimal management of bladder retention following vaginal prolapse surgery: a randomized controlled trial comparing clean intermittent catheterization (CIC) and transurethral indwelling catheterisation (TIC) (Abstract number 58). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2010;29(6):892‐3. [40128]
-
- Hakvoort RA, Thijs SSD, Bouwmeester FW, Broekman AM, Ruhe IM, Vernooij MM, et al. Comparing clean intermittent catheterisation and transurethral indwelling catheterisation for incomplete voiding after vaginal prolapse surgery: a multicentre randomised trial. BJOG 2011;118(9):1055‐60. [sr‐incont42075] - PubMed
-
- NTR1152. A randomised trial determining whether intermittent catheterisation is a better option for treating urinary retention than a transurethral indwelling bladder catheter for the outcomes duration of catheterisation, urinary tract infection and patient satisfaction ‐ CATH trial. www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=1152 (accessed 12th November 2015). [NTR1152; sr‐incont65505]
Halleberg 2013 {published data only}
-
- Halleberg Nyman M, Gustafsson M, Langius‐Eklof A, Johansson JE, Norlin R, Hagberg L. Intermittent versus indwelling urinary catheterisation in hip surgery patients: a randomised controlled trial with cost‐effectiveness analysis. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2013;50(12):1589‐98. [sr‐incont61995] - PubMed
Hammarsten 1992 {published data only}
-
- Hammarsten J, Lindqvist K. Suprapubic catheter following transurethral resection of the prostate: a way to decrease the number of urethral strictures and improve the outcome of operations. Journal of Urology 1992;147(3):651‐2. [sr‐incont1271] - PubMed
Harms 1985 {published data only}
-
- Harms E, Christmann U, Klock FK. Suprapubic urinary diversion following gynecologic operations. [German]. Geburtshilfe und Frauenheilkunde 1985;45(4):254‐60. [sr‐incont1140] - PubMed
Ichsan 1987 {published data only}
-
- Ichsan J, Hunt DR. Suprapubic catheters: a comparison of suprapubic versus urethral catheters in the treatment of acute urinary retention. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Surgery 1987;57(1):33‐6. - PubMed
Jannelli 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jannelli ML, Wu JM, Plunkett LW, Williams KS, Visco AG. A randomized controlled trial of clean intermittent self‐catheterization versus suprapubic catheterization after urogynecologic surgery. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2007;197(1):72‐4. [sr‐incont23807] - PubMed
Katz 1992 {published data only}
-
- Katz G, Milgalter E, Landau Y, Borman JB. Prevention of urethral strictures following coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Urology 1992;39(5):433‐5. - PubMed
Kerr‐Wilson 1986 {published data only}
-
- Kerr‐Wilson RH, McNally S. Bladder drainage for caesarean section under epidural analgesia. BJOG 1986;93(1):28‐30. - PubMed
Knight 1996 {published data only}
-
- Knight RM, Pellegrini VD Jr. Bladder management after total joint arthroplasty. Journal of Arthroplasty 1996;11(8):882‐8. [sr‐incont4765] - PubMed
Korkes 2008 {published data only}
-
- Korkes F, Moniz RR, Silva FA, Guidoni LRM, Silva DB, Fernandes RC, et al. Urethral vs suprapubic catheter following open prostatectomy: surgeon's choice. Revista Chilena de Urologia 2008;73(4):272‐6. [sr‐incont39873]
Kringel 2010 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN46098701. Comparison of the postoperative rate of complications and infections in indwelling urinary catheters and suprapubic catheters after anterior colporrhaphia: a three‐arm prospective randomised trial. isrctn.org/ISRCTN46098701 (accessed 12th November 2015). [ISRCTN46098701; sr‐incont62940 ]
-
- Kringel U, Reuimer T, Tomczak S, Green S, Kundt G, Gerber B. Postoperative infections due to bladder catheters after anterior colporrhaphy: a prospective, randomized three‐arm study. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 2010;21(12):1499‐504. [ISRCTN46098701; sr‐incont41072] - PubMed
Michelson 1988 {published data only}
-
- Michelson JD, Lotke PA, Steinberg ME. Urinary‐bladder management after total joint‐replacement surgery. New England Journal of Medicine 1988;319(6):321‐6. - PubMed
Millet 2012 {published data only}
-
- Millet L, Shah S, Bartholomew ML. Rates of bacteriuria in laboring women with epidural analgesia: continuous vs. intermittent bladder catheterization. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2012;206(4):316.e1‐7. [sr‐incont44529] - PubMed
-
- Millet L, Shaha S, Bartholomew ML. Bacteriuria in laboring women with epidural analgesia: Continuous vs intermittent bladder catheterization (Abstract number 52). American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2012;206(1 Suppl 1):S33. [sr‐incont65102] - PubMed
Naik 2005 {published data only}
-
- Naik R, Maughan K, Nordin A, Lopes A, Godfrey KA, Hatem MH. A prospective randomised controlled trial of intermittent self‐catheterisation vs. supra‐pubic catheterisation for post‐operative bladder care following radical hysterectomy. Gynecologic Oncology 2005;99(2):437‐42. [sr‐incont21564] - PubMed
-
- Roberts K, Naik R. Catheterization options following radical surgery for cervical cancer. British Journal of Nursing 1006;15(19):1038‐44. [sr‐incont22222] - PubMed
Nwabineli 1993 {published data only}
-
- Nwabineli NJ, Walsh DJ, Davis JA. Urinary drainage following radical hysterectomy for cervical carcinoma ‐ A pilot comparison of urethral and suprapubic routes. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer 1993;3(4):208‐10. [sr‐incont7143] - PubMed
O'Kelly 1995 {published data only}
-
- O'Kelly TJ, Mathew A, Ross S, Munro A. Optimum method for urinary drainage in major abdominal surgery: a prospective randomized trial of suprapubic versus urethral catheterization. British Journal of Surgery 1995;82(10):1367‐8. [sr‐incont2866] - PubMed
Perrin 1997 {published data only}
-
- Perrin LC, Penfold C, McLeish A. A prospective randomized controlled trial comparing suprapubic with urethral catheterization in rectal surgery. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Surgery 1997;67(8):554‐6. [sr‐incont5587] - PubMed
Piergiovanni 1991 {published data only}
-
- Piergiovanni M, Tschantz P. [Urinary catheterization: transurethral or suprapubic approach?]. [French]. Helvetica Chirurgica Acta 1991;58(1‐2):201‐5. [sr‐incont1280] - PubMed
Prasad 2014 {published data only}
-
- Prasad SM, Large MC, Patel AR, Famakinwa O, Galocy RM, Karrison T, et al. Early removal of urethral catheter with suprapubic tube drainage versus urethral catheter drainage alone after robot‐assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Journal of Urology 2014;192(1):89‐95. [sr‐incont66322] - PubMed
Rasmussen 1977 {published data only}
-
- Rasmussen OV, Korner B, Møller‐Sørensen P, Kronborg O. Suprapubic versus urethral bladder drainage following surgery for rectal cancer. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica 1977;143(6):371‐4. - PubMed
Ratnaval 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ratnaval CD, Renwick P, Farouk R, Monson JR, Lee PW. Suprapubic versus transurethral catheterisation of males undergoing pelvic colorectal surgery. International Journal of Colorectal Disease 1996;11(4):177‐9. - PubMed
Rivard 2012 {published data only}
-
- NCT00959920. Study of obstetric Foley therapy (SOFT trial). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00959920 (accessed 12th November 2015). [NCT00959920; TrialID.SOFT; sr‐incont64492]
-
- Rivard C, Awad M, Liebermann M, Dejong M, Massey SM, Sinacore J, et al. Bladder drainage during labor: a randomized controlled trial. The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2012;38(8):1046‐51. [NCT00959920; sr‐incont49710] - PubMed
Schiotz 1989 {published data only}
-
- Schiotz HA, Malme PA, Tanbo TG. Urinary tract infections and asymptomatic bacteriuria after vaginal plastic surgery. A comparison of suprapubic and transurethral catheters. Acta Obstetricia Gynecologica Scandinavica 1989;68(5):453‐5. [sr‐incont1165] - PubMed
Sethia 1987 {published data only}
-
- Sethia KK, Selkon JB, Berry AR, Turner CM, Kettlewell MG, Gough MH. Prospective randomized controlled trial of urethral versus suprapubic catheterization. British Journal of Surgery 1987;74(7):624‐5. [sr‐incont1114] - PubMed
Skelly 1992 {published data only}
Stekkinger 2011 {published data only}
-
- NTR1528. A comparison of suprapubic and transurethral catheterization on postoperative urinary retention after vaginal prolapse repair ‐ CAD TRIAL. www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=1528 (accessed 12th November 2015). [NTR1528; sr‐incont65499] - PubMed
-
- Stekkinger E, Linden PJQ. A comparison of suprapubic and transurethral catheterization after vaginal prolapse repair: a randomized controlled trial. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 2011;72(2):109‐16. [sr‐incont42069] - PubMed
Tang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tang MW, Kwok TC, Hui E, Woo J. Intermittent versus indwelling catheterization in older female patients. Maturitas 2006;53(3):274‐81. [sr‐incont22495] - PubMed
Tangtrakul 1994 {published data only}
-
- Tangtrakul S, Taechaiya S, Suthutvoravut S, Linasmita V. Post‐cesarean section urinary tract infection: a comparison between intermittent and indwelling catheterization. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1994;77(5):244‐8. - PubMed
Van den Brand 2001 {published data only}
-
- Brand I, Castelein RM. Total joint arthroplasty and incidence of postoperative bacteriuria with an indwelling catheter or intermittent catheterization with one‐dose antibiotic prophylaxis: a prospective randomized trial. Journal of Arthroplasty 2001;16(7):850‐5. [sr‐incont13007] - PubMed
Vandoni 1994 {published data only}
-
- Vandoni RE, Lironi A, Tschantz P. Bacteriuria during urinary tract catheterization: suprapubic versus urethral route: a prospective randomized trial. Acta Chirurgica Belgica 1994;94(1):12‐6. [sr‐incont30] - PubMed
Wiser 1974 {published data only}
-
- Wiser WL, Morrison JC, Loveday GL, McIntosh RE, Kennedy BS, Shaw BH, et al. Management of bladder drainage following vaginal plastic repairs. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1974;44(1):65‐71. [sr‐incont874] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abrams 1980 {published data only}
Allardice 1988 {published data only}
Cardenas 2010 {published data only}
-
- Cardenas D, Moore KN, Dannels‐McClure A, Scelza W, Granves D, Brooks M. Intermittent catheterisation with hydrophilic‐coated catheters delays the onset of urinary tract infection in patients with acute spinal cord injury: an international, multicenter, randomised controlled trial (Abstract number 126). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2010;29(6):990‐1. [sr‐incont40143]
Chartier‐Kastler 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chartier‐Kastler E, Lauge I, Ruffion A, Goossens D, Charvier K, Biering‐Sorensen F. Safety of a new compact catheter for men with neurogenic bladder dysfunction: a randomised, crossover and open‐labelled study. Spinal Cord 2011;49(7):844‐50. [NCT00990093; sr‐incont42729] - PubMed
Dunn 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dunn TS, Shlay J, Forshner D. Are in‐dwelling catheters necessary for 24 hours after hysterectomy?. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;189(2):435‐7. - PubMed
Frymire 1971 {published data only}
-
- Frymire LJ. Comparison of suprapubic versus Foley drains. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1971;38(2):239‐44. - PubMed
Ghalayini 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ghalayini IF, Al Ghazo MA, Pickard RS. A prospective randomized trial comparing tranurethral prostatic resection and clean intermittent self‐catheterization in men with chronic urinary retention. BJU International 2005;96(1):93‐7. [sr‐incont21452] - PubMed
Grundy 1983 {published data only}
-
- Grundy DJ, Fellows GJ, Gillett AP, Nuseibeh I, Silver JR. A comparison of fine‐bore suprapubic and an intermittent urethral catheterisation regime after spinal cord injury. Paraplegia 1983;21(4):227‐32. [sr‐incont7525] - PubMed
Hofmeister 1970 {published data only}
-
- Hofmeister FJ, Martens WE, Strebel RL. Foley catheter or suprapubic tube?. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1970;107(5):767‐79. - PubMed
Horgan 1992 {published data only}
-
- Horgan AF, Prasad B, Waldron DJ, O'Sullivan DC. Acute urinary retention. Comparison of suprapubic and urethral catheterisation. British Journal of Urology 1992;70(2):149‐51. [sr‐incont18523] - PubMed
Park 2010 {published data only}
Schumm 2008 {published data only}
-
- Schumm K, N'Dow J, Norrie J, and the CATHETER Study Group. Recruitment challenges in a large randomsed controlled trial with complex processes (Abstract number P06). Proceedings of the 29th Society for Clinical Trials Annual Meetibng, 18‐21 May 2008, St. Louis (MO). 2008. [sr‐incont27304]
Shapiro 1982 {published data only}
-
- Shapiro J, Hoffmann J, Jersky J. A comparison of suprapubic and transurethral drainage for postoperative urinary retention in general surgical patients. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica 1982;148(4):323‐7. [sr‐incont46935] - PubMed
Sicilia 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sicilia I, Mattioni A, Cenciarelli S, Mazzoli T, Gallinella E, Greco LM, et al. Intermittent versus permanent bladder catheterization in acute stroke patients (Abstract number 600). Cerebrovascular Diseases 2013;35(Suppl 3):663. [sr‐incont59886]
Suprasert 2002 {published data only}
-
- Suprasert P, Srisomboon J, Phongnarisorn C. A prospective randomized study comparing voiding time between suprapubic catheterization and intermittent self‐catheterization following radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy for cervical cancer. Thai Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 2002;14(1):73‐9. [sr‐incont26731]
Turi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Turi MH, Hanif S, Fasih Q, Shaikh MA. Proportion of complications in patients practicing clean intermittent self‐catheterization (CISC) vs indwelling catheter. Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2006;56(9):401‐9. [sr‐incont22267] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Kringel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kringel U, Gerber B. Comparision of the postoperative rate of complications and infections in indwelling urinary catheters and suprapubic catheters after anterior kolporrhaphia: a 3‐arm prospective randomised trial. Interim analysis after 30 patients (Abstract: Poster presentation). Proceedings of the North German Society of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (NGGG) meeting, 2007 Sept 7‐9, Göttingen, Germany. 2007. [ISRCTN46098701; sr‐incont64686]
References to ongoing studies
ACTRN12614000618651 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12614000618651. Randomized control trial of continuous indwelling urinary catheter versus intermittent urinary catheter in pregnant women during epidural anesthesia in labour to prevent severe post partum urinary retention. www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12614000618651.aspx (accessed 12th November 2015). [ACTRN12614000618651; sr‐incont62933]
NCT01465594 2011 {published data only}
-
- NCT01465594. Randomized study comparing urinary diversion by suprapubic catheter with transurethral catheter in patients after radical prostatectomy. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01465594 (accessed 12th November 2015). [NCT01465594; sr‐incont50317]
NCT02108431 2013 {published data only}
-
- NCT02108431, Habibzada J, Godes M, Witt JH. Superior postoperative patient comfort in suprapubic drainage versus transurethral catheterization following robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy: a prospective randomized clinical trial. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02108431 (accessed 12th November 2015). [NCT02108431; sr‐incont60954] - PubMed
NCT02198157 2014 {published data only}
-
- NCT02198157. Effect of intermittent versus continuous bladder catheterization during labor on second stage duration. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02198157 (accessed 12th November 2015). [NCT02198157; sr‐incont62945]
NTR2806 {published data only}
-
- NTR2806. Catheter Management and complications for Symptomatic Postpartum Urinary Retention ‐ CAMPUR. www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=2806 (accessed 12th November 2015). [NTR2806; TrialID.CAMPUR.; sr‐incont66314]
Wilson 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wilson B, Phelps C. Identifying and applying a targeted evidence‐based practice change in the maternal/child health inpatient setting. Nursing for Women's Health 2013;17(6):490‐7. [sr‐incont65833] - PubMed
Additional references
Ahluwalia 2006
CDC 2015
-
- National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Urinary tract infection (Catheter‐Associated Urinary Tract Infection [CAUTI] and Non‐Catheter‐Associated Urinary Tract Infection [UTI]) and other urinary system infection [USI]) events, Chapter 7 ‐ 13 device‐associated module. CDC NHSN Patient Safety Component (PSC) Manual. Atlanta, GA. (available at: cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscManual/7pscCAUTIcurrent.pdf) (accessed 4 February 2015): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 5 January 2015.
COMET
-
- Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials (COMET) Initiative. COMET Initiative. www.comet‐initiative.org/ (accessed 27 May 2015).
EAU 2014
-
- European Assocation of Urology. EAU Guidelines. 25th Edition. Arnhem, The Netherlands: EAU Guidelines Office, 2014.
Elvy 2009
-
- Elvy J, Colville A. Catheter associated urinary tract infection: what is it, what causes it and how can we prevent it?. Journal of Infection Prevention 2009;10(2):36‐41.
Geng 2006
-
- Geng V, Emblem EL, Gratzl S, Incesu O, Jensen K. EAUN Good Practice in Healthcare: Urethral Catheterisation. Section 2: Male, female and paediatric intermittent catheterization. Arnhem, The Netherlands: European Assocation of Urology, 2006.
Geng 2012
-
- Geng V, Cobussen‐Boekhorst H, Farrell J, Gea‐Sanchez M, Pearce I, Schwennesen T, et al. Catheterisation ‐ Indwelling catheters in adults: urethral and suprapubic. 1st Edition. Arnhem, The Netherlands: European Association of Urology Nurses, 2012.
Gould 2009
-
- Gould CV, Umscheid CA, Agarwal RK, Kunst G, Pegues DA, and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC). Guideline for Prevention of Catheter‐Associated Urinary Tract Infections 2009. cdc.gov/hicpac/pdf/CAUTI/CAUTIguideline2009final.pdf. Atlanta, GA: Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), (accessed 4th February 2015).
Grabe 2015
-
- Grabe M, Bartoletti R, Bjerklund Johansen TE, Cai T, Cek M, Koves B, et al. Urological infections. In: European Assocation of Urology, editor(s). European Association of Urology Guidelines. 2015 Edition. Arnhem, The Netherlands: EAU Guidelines Office, 2015:7‐13.
Harrison 2011
-
- Harrison SCW, Lawrence WT, Morley R, Pearce I, Taylor J. British Association of Urological Surgeons' suprapubic catheter practice guidelines. BJU International 2011;107(1):77‐85. - PubMed
Health Committee 2013
-
- Health Committee, House of Commons. Written evidence from Bard Ltd (PEX 17) (2012 Oct); Eleventh report of session 2012‐13 ‐ Public expenditure on health and care services – Volume II ‐ Additional written evidence (HC 2012‐13, 651). www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201213/cmselect/cmhealth/651/651vw.pdf. London: The Stationery Office Limited, (accessed 28 May 2015).
Healy 2012
-
- Healy EF, Walsh CA, Cotter AM, Walsh SR. Suprapubic compared with transurethral bladder catheterization for gynecologic surgery: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2012;120(3):678‐87. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Hooton 2010
-
- Hooton TM, Bradley SF, Cardenas DD, Colgan R, Geerlings SE, Rice JC, et al. Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of catheter‐associated urinary tract infections in adults: 2009 International Clinical Practice Guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2010;50(5):625‐63. - PubMed
Lam 2014
Lusardi 2013
McPhail 2006
-
- McPhail M J, Abu‐Hilal M, Johnson CD. A meta‐analysis comparing suprapubic and transurethral catheterization for bladder drainage after abdominal surgery. British Journal of Surgery 2006;93(9):1038‐44. - PubMed
Nasr 2010
Newman 2010
-
- Newman DK. Prevention and management of catheter‐associated UTIs. Infectious Disease 2010;Special Edition:13‐20.
Nicolle 2005
-
- Nicolle LE, Bradley S, Colgan R, Rice JC, Schaeffer A, Hooton TM. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in adults. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2005;40(5):643‐54. - PubMed
Omar 2013
-
- Omar MI, Lam TBL, MacLennan S. Critical outcomes in a Cochrane systematic review: patients' perspective. 21st Cochrane Colloquium 2013;Suppl:2.
Phipps 2006
Reference Manager 2012 [Computer program]
-
- Thomson Reuters. Reference Manager Professional Edition. Version Version 12. New York: Thomson Reuters, 2012.
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Smyth 2008
-
- Smyth E, McIlveny G, Enstone J, Emmerson A, Humphreys H, Fitzpatrick F, et al. Hospital Infection Society Prevalence Survey Steering Group. Four country healthcare associated infection prevalence survey 2006: overview of the results. Journal of Hospital Infection 2008;69(3):230‐48. - PubMed
Tambyah 1999
-
- Tambyah PA, Halvorson KT, Maki DG. A prospective study of pathogenesis of catheter‐associated urinary tract infections. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 1999;74(2):131‐6. [15410] - PubMed
Tenke 2008
-
- Tenke P, Kovacs B, Bjerklund Johansen TE, Matsumoto T, Tambyah PA, Naber KG. European and Asian guidelines on management andprevention of catheter‐associated urinary tract infections. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2008;31(1):68‐78. - PubMed
Trautner 2004
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐item short‐form health survey (SF‐36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care 1992;30(6):473‐83. - PubMed
Warren 2001
-
- Warren JW. Catheter‐associated urinary tract infections. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2001;17(4):299‐303. [15414] - PubMed
Zigmond 1983
-
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67(6):361‐70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

