Cell-specific regulation of L-WNK1 by dietary K
- PMID: 26662201
- PMCID: PMC4675801
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00226.2015
Cell-specific regulation of L-WNK1 by dietary K
Abstract
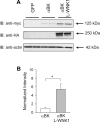
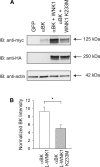
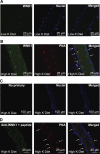
Flow-induced K(+) secretion in the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron is mediated by high-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK) channels. Familial hyperkalemic hypertension (pseudohypoaldosteronism type II) is an inherited form of hypertension with decreased K(+) secretion and increased Na(+) reabsorption. This disorder is linked to mutations in genes encoding with-no-lysine kinase 1 (WNK1), WNK4, and Kelch-like 3/Cullin 3, two components of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that degrades WNKs. We examined whether the full-length (or "long") form of WNK1 (L-WNK1) affected the expression of BK α-subunits in HEK cells. Overexpression of L-WNK1 promoted a significant increase in BK α-subunit whole cell abundance and functional channel expression. BK α-subunit abundance also increased with coexpression of a kinase dead L-WNK1 mutant (K233M) and with kidney-specific WNK1 (KS-WNK1), suggesting that the catalytic activity of L-WNK1 was not required to increase BK expression. We examined whether dietary K(+) intake affected L-WNK1 expression in the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron. We found a paucity of L-WNK1 labeling in cortical collecting ducts (CCDs) from rabbits on a low-K(+) diet but observed robust staining for L-WNK1 primarily in intercalated cells when rabbits were fed a high-K(+) diet. Our results and previous findings suggest that L-WNK1 exerts different effects on renal K(+) secretory channels, inhibiting renal outer medullary K(+) channels and activating BK channels. A high-K(+) diet induced an increase in L-WNK1 expression selectively in intercalated cells and may contribute to enhanced BK channel expression and K(+) secretion in CCDs.
Keywords: high-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels; kidney-specific with-no-lysine kinase 1; long with-no-lysine kinase 1; potassium adaptation; pseudohypoaldosteronism; with-no-lysine kinase 1.
Figures




References
-
- Alessi DR, Zhang J, Khanna A, Hochdorfer T, Shang Y, Kahle KT. The WNK-SPAK/OSR1 pathway: master regulator of cation-chloride cotransporters. Sci Signal 7: 3, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson NS, Robertson GA, Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science 253: 551–555, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Beck FX, Dorge A, Blumner E, Giebisch G, Thurau K. Cell rubidium uptake: a method for studying functional heterogeneity in the nephron. Kidney Int 33: 642–651, 1988. - PubMed
-
- Boim MA, Ho K, Shuck ME, Bienkowski MJ, Block JH, Slightom JL, Yang Y, Brenner BM, Hebert SC. ROMK inwardly rectifying ATP-sensitive K+ channel. II. Cloning and distribution of alternative forms. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 268: F1132–F1140, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Boyden LM, Choi M, Choate KA, Nelson-Williams CJ, Farhi A, Toka HR, Tikhonova IR, Bjornson R, Mane SM, Colussi G, Lebel M, Gordon RD, Semmekrot BA, Poujol A, Valimaki MJ, De Ferrari ME, Sanjad SA, Gutkin M, Karet FE, Tucci JR, Stockigt JR, Keppler-Noreuil KM, Porter CC, Anand SK, Whiteford ML, Davis ID, Dewar SB, Bettinelli A, Fadrowski JJ, Belsha CW, Hunley TE, Nelson RD, Trachtman H, Cole TR, Pinsk M, Bockenhauer D, Shenoy M, Vaidyanathan P, Foreman JW, Rasoulpour M, Thameem F, Al-Shahrouri HZ, Radhakrishnan J, Gharavi AG, Goilav B, Lifton RP. Mutations in kelch-like 3 and cullin 3 cause hypertension and electrolyte abnormalities. Nature 482: 98–102, 2012. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 DK051391/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-084184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DK-091202/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37-DK-051391/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-098145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK084060/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK091202/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK038470/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-038470/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

