Tenacibaculum finnmarkense sp. nov., a fish pathogenic bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from Atlantic salmon
- PMID: 26662517
- PMCID: PMC4751178
- DOI: 10.1007/s10482-015-0630-0
Tenacibaculum finnmarkense sp. nov., a fish pathogenic bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from Atlantic salmon
Abstract
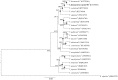
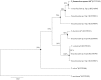
A novel Gram-stain negative, aerobic, non-flagellated, rod-shaped gliding bacterial strain, designated HFJ(T), was isolated from a skin lesion of a diseased Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in Finnmark, Norway. Colonies were observed to be yellow pigmented with entire and/or undulating margins and did not adhere to the agar. The 16S rRNA gene sequence showed that the strain belongs to the genus Tenacibaculum (family Flavobacteriaceae, phylum 'Bacteroidetes'). Strain HFJ(T) exhibits high 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity values to Tenacibaculum dicentrarchi NCIMB 14598(T) (97.2 %). The strain was found to grow at 2-20 °C and only in the presence of sea salts. The respiratory quinone was identified as menaquinone 6 and the major fatty acids were identified as summed feature 3 (comprising C16:1 ω7c and/or iso-C15:0 2-OH), iso-C15:0, anteiso-C15:0, iso-C15:1 and iso-C15:0 3-OH. The DNA G+C content was determined to be 34.1 mol%. DNA-DNA hybridization and comparative phenotypic and genetic tests were performed with the phylogenetically closely related type strains, T. dicentrarchi NCIMB 14598(T) and Tenacibaculum ovolyticum NCIMB 13127(T). These data, as well as phylogenetic analyses, suggest that strain HFJ(T) should be classified as a representative of a novel species in the genus Tenacibaculum, for which the name Tenacibaculum finnmarkense sp. nov. is proposed; the type strain is HFJ (T) = (DSM 28541(T) = NCIMB 42386(T)).
Keywords: Norway; Polyphasic taxonomy; Salmon farming; Skin lesions; Ulcerative disease; Winter ulcers.
Figures

References
-
- Bernardet J-F, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B. Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol. 2002;52:1049–1070. - PubMed
-
- Bornø G, Lie LM. Fish health report 2014. Harstad: The Norwegain Veterinary Institute; 2015.
-
- Bruno DW, Noguera PA, Poppe TT. A color Atlas of salmonid diseases. 2. Dordrecht: Springer; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

