Endothelin regulates intermittent hypoxia-induced lipolytic remodelling of adipose tissue and phosphorylation of hormone-sensitive lipase
- PMID: 26663321
- PMCID: PMC4799974
- DOI: 10.1113/JP271321
Endothelin regulates intermittent hypoxia-induced lipolytic remodelling of adipose tissue and phosphorylation of hormone-sensitive lipase
Abstract
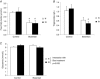
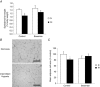
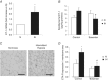
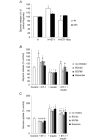
Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome is characterized by repetitive episodes of upper airway collapse during sleep resulting in chronic intermittent hypoxia (IH). Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome, through IH, promotes cardiovascular and metabolic disorders. Endothelin-1 (ET-1) secretion is upregulated by IH, and is able to modulate adipocyte metabolism. Therefore, the present study aimed to characterize the role of ET-1 in the metabolic consequences of IH on adipose tissue in vivo and in vitro. Wistar rats were submitted to 14 days of IH-cycles (30 s of 21% FiO2 and 30 s of 5% FiO2 ; 8 h day(-1) ) or normoxia (air-air cycles) and were treated or not with bosentan, a dual type A and B endothelin receptor (ETA-R and ETB-R) antagonist. Bosentan treatment decreased plasma free fatty acid and triglyceride levels, and inhibited IH-induced lipolysis in adipose tissue. Moreover, IH induced a 2-fold increase in ET-1 transcription and ETA-R expression in adipose tissue that was reversed by bosentan. In 3T3-L1 adipocytes, ET-1 upregulated its own and its ETA-R transcription and this effect was abolished by bosentan. Moreover, ET-1 induced glycerol release and inhibited insulin-induced glucose uptake. Bosentan and BQ123 inhibited these effects. Bosentan also reversed the ET-1-induced phosphorylation of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) on Ser(660) . Finally, ET-1-induced lipolysis and HSL phosphorylation were also observed under hypoxia. Altogether, these data suggest that ET-1 is involved in IH-induced lipolysis in Wistar rats, and that upregulation of ET-1 production and ETA-R expression by ET-1 itself under IH could amplify its effects. Moreover, ET-1-induced lipolysis could be mediated through ETA-R and activation of HSL by Ser(660) phosphorylation.
© 2015 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2015 The Physiological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Anthonsen MW, Ronnstrand L, Wernstedt C, Degerman E & Holm C (1998). Identification of novel phosphorylation sites in hormone‐sensitive lipase that are phosphorylated in response to isoproterenol and govern activation properties in vitro. J Biol Chem 273, 215–221. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud C, Poulain L, Levy P & Dematteis M (2011). Inflammation contributes to the atherogenic role of intermittent hypoxia in apolipoprotein‐E knock out mice. Atherosclerosis 219, 425–431. - PubMed
-
- Belaidi E, Joyeux‐Faure M, Ribuot C, Launois SH, Levy P & Godin‐Ribuot D (2009). Major role for hypoxia inducible factor‐1 and the endothelin system in promoting myocardial infarction and hypertension in an animal model of obstructive sleep apnea. J Am Coll Cardiol 53, 1309–1317. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya I & Ullrich A (2006). Endothelin‐1 inhibits adipogenesis: role of phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2. FEBS Lett 580, 5765–5771. - PubMed
-
- Campo A, Fruhbeck G, Zulueta JJ, Iriarte J, Seijo LM, Alcaide AB, Galdiz JB & Salvador J (2007). Hyperleptinaemia, respiratory drive and hypercapnic response in obese patients. Eur Respir J 30, 223–231. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

