Reductions in Mean 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure After 6-Week Treatment With Canagliflozin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension
- PMID: 26663712
- PMCID: PMC8032082
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.12747
Reductions in Mean 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure After 6-Week Treatment With Canagliflozin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension
Abstract
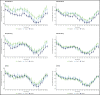
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluated the early effects of canagliflozin on blood pressure (BP) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and hypertension. Patients were randomized to canagliflozin 300 mg, canagliflozin 100 mg, or placebo for 6 weeks and underwent 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring before randomization, on day 1 of treatment, and after 6 weeks. The primary endpoint was change in mean 24-hour systolic BP (SBP) from baseline to week 6. Overall, 169 patients were included (mean age, 58.6 years; glycated hemoglobin, 8.1%; seated BP 138.5/82.7 mm Hg). At week 6, canagliflozin 300 mg provided greater reductions in mean 24-hour SBP than placebo (least squares mean -6.2 vs -1.2 mm Hg, respectively; P=.006). Numerical reductions in SBP were observed with canagliflozin 100 mg. Canagliflozin was generally well tolerated, with side effects similar to those reported in previous studies. These results suggest that canagliflozin rapidly reduces BP in patients with T2DM and hypertension.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Comment in
-
Response to Stavropoulos.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016 Oct;18(10):1074-1075. doi: 10.1111/jch.12831. Epub 2016 Apr 21. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016. PMID: 27098365 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Canagliflozin and Hypertension: Is It the Optimal Choice for All Hypertensive Patients?J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016 Oct;18(10):1073. doi: 10.1111/jch.12832. Epub 2016 Apr 21. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2016. PMID: 27098448 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kabakov E, Norymberg C, Osher E, et al. Prevalence of hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus: impact of the tightening definition of high blood pressure and association with confounding risk factors. J Cardiometab Syndr. 2006;1:95–101. - PubMed
-
- Ferrannini E, Cushman WC. Diabetes and hypertension: the bad companions. Lancet. 2012;380:601–610. - PubMed
-
- Vasilakou D, Karagiannis T, Athanasiadou E, et al. Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:262–274. - PubMed
-
- Baker WL, Smyth LR, Riche DM, et al. Effects of sodium–glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitors on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014;8:262–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

