Resveratrol and liver: A systematic review
- PMID: 26664429
- PMCID: PMC4652315
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-1995.168405
Resveratrol and liver: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Recent studies demonstrated that resveratrol has many therapeutic effects on liver disorders. Resveratrol significantly increased survival after liver transplantation, decreased fat deposition, necrosis, and apoptosis which induced by ischemia in Wistar rats. It provided liver protection against chemical, cholestatic, and alcohol injury. Resveratrol can improve glucose metabolism and lipid profile and decrease liver fibrosis and steatosis. Furthermore, it was able to alter hepatic cell fatty acid composition. According to extension of liver disease around the world and necessity of finding new threat, this review critically examines the current preclinical in vitro and in vivo studies on the preventive and therapeutic effects of resveratrol in liver disorders.
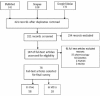
Materials and methods: A search in PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus was undertaken to identify relevant literature using search terms, including "liver," "hepatic," and "Resveratrol." Both in vivo and in vitro studies were included. No time limiting considered for this search.
Results: A total of 76 articles were eligible for this review. In these articles, resveratrol shows antioxidative properties in different models of hepatitis resulting in reducing of hepatic fibrosis.
Conclusion: Resveratrol could reduce hepatic steatosis through modulating the insulin resistance and lipid profile in animals. These high quality preclinical studies propose the potential therapeutic implication of resveratrol in liver disorders especially those with hepatic steatosis. Resveratrol can play a pivotal role in prevention and treatment of liver disorders by reducing hepatic fibrosis.
Keywords: Antioxidant; fibrosis; liver; liver disorders; liver dysfunction; liver transplantation; nonalcoholic fatty liver; resveratrol; steatosis.
References
-
- Luther DJ, Ohanyan V, Shamhart PE, Hodnichak CM, Sisakian H, Booth TD, et al. Chemopreventive doses of resveratrol do not produce cardiotoxicity in a rodent model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29:380–91. - PubMed
-
- Wang G, Guo X, Chen H, Lin T, Xu Y, Chen Q, et al. A resveratrol analog, phoyunbene B, induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 liver cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012;22:2114–8. - PubMed
-
- Baur JA, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:493–506. - PubMed
-
- Shankar S, Singh G, Srivastava RK. Chemoprevention by resveratrol: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Front Biosci. 2007;12:4839–54. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources