C-H bond halogenation catalyzed or mediated by copper: an overview
- PMID: 26664634
- PMCID: PMC4661017
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.11.230
C-H bond halogenation catalyzed or mediated by copper: an overview
Abstract
Carbon-halogen (C-X) bonds are amongst the most fundamental groups in organic synthesis, they are frequently and widely employed in the synthesis of numerous organic products. The generation of a C-X bond, therefore, constitutes an issue of universal interest. Herein, the research advances on the copper-catalyzed and mediated C-X (X = F, Cl, Br, I) bond formation via direct C-H bond transformation is reviewed.
Keywords: C(sp2)–H bond; C(sp3)–H bond; copper; halogenation.
Figures








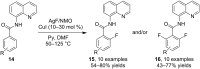


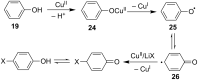










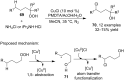
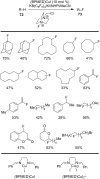

References
-
- Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. 6th ed. Wiley-VCH; 2002.
-
- Davos S G. Organotransition Metal Chemistry: Application to Organic Synthesis. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1982.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
