Shared Decision Making in mental health care using Routine Outcome Monitoring as a source of information: a cluster randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 26666295
- PMCID: PMC4678650
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-015-0696-2
Shared Decision Making in mental health care using Routine Outcome Monitoring as a source of information: a cluster randomised controlled trial
Abstract
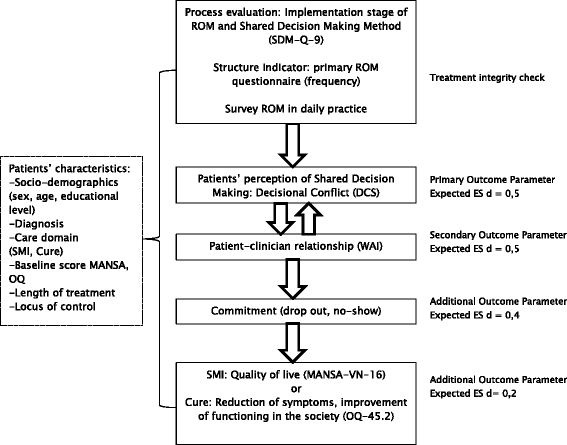
Background: Shared Decision Making (SDM) is a way to empower patients when decisions are made about treatment. In order to be effective agents in this process, patients need access to information of good quality. Routine Outcome Monitoring (ROM) may provide such information and therefore may be a key element in SDM. This trial tests the effectiveness of SDM using ROM, primarily aiming to diminish decisional conflict of the patient while making decisions about treatment. The degree of decisional conflict, the primary outcome of this study, encompasses personal certainty about choosing an appropriate treatment, information about options, clarification of patient values, support from others and patients experience of an effective decision making process. Secondary outcomes of the study focus on the working alliance between patient and clinician, adherence to treatment, and clinical outcome and quality of life.
Methods/design: This article presents the study protocol of a multi-centre two-arm cluster randomised controlled trial (RCT). The research is conducted in Dutch specialised mental health care teams participating in the ROM Quality Improvement Collaborative (QIC), which aims to implement ROM in daily clinical practice. In the intervention teams, ROM is used as a source of information during the SDM process between the patient and clinician. Control teams receive no specific SDM or ROM instructions and apply decision making as usual. Randomisation is conducted at the level of the participating teams within the mental health organisations. A total of 12 teams from 4 organisations and 364 patients participate in the study. Prior to data collection, the intervention teams are trained to use ROM during the SDM process. Data collection will be at baseline, and at 3 and 6 months after inclusion of the patient. Control teams will implement the SDM and ROM model after completion of the study.
Discussion: This study will provide useful information about the effectiveness of ROM within a SDM framework. Furthermore, with practical guidelines this study may contribute to the implementation of SDM using ROM in mental health care. Reporting of the results is expected from December 2016 onwards.
Trial registration: Dutch trial register: TC5262. Trial registration date: 24th of June 2015.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical