The role of HCV proteins on treatment outcomes
- PMID: 26666318
- PMCID: PMC4678629
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-015-0450-x
The role of HCV proteins on treatment outcomes
Abstract
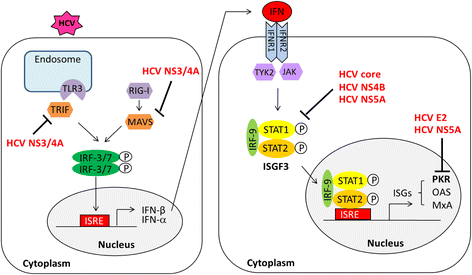
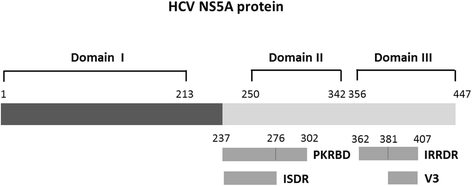
For many years, the standard of treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection was a combination of pegylated interferon alpha (Peg-IFN-α) and ribavirin for 24-48 weeks. This treatment regimen results in a sustained virologic response (SVR) rate in about 50% of cases. The failure of IFN-α-based therapy to eliminate HCV is a result of multiple factors including a suboptimal treatment regimen, severity of HCV-related diseases, host factors and viral factors. In recent years, advances in HCV cell culture have contributed to a better understanding of the viral life cycle, which has led to the development of a number of direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) that target specific key components of viral replication, such as HCV NS3/4A, HCV NS5A, and HCV NS5B proteins. To date, several new drugs have been approved for the treatment of HCV infection. Application of DAAs with IFN-based or IFN-free regimens has increased the SVR rate up to >90% and has allowed treatment duration to be shortened to 12-24 weeks. The impact of HCV proteins in response to IFN-based and IFN-free therapies has been described in many reports. This review summarizes and updates knowledge on molecular mechanisms of HCV proteins involved in anti-IFN activity as well as examining amino acid variations and mutations in several regions of HCV proteins associated with the response to IFN-based therapy and pattern of resistance associated amino acid variants (RAV) to antiviral agents.
Figures

References
-
- Moriya K, Yotsuyanagi H, Shintani Y, Fujie H, Ishibashi K, Matsuura Y, et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein induces hepatic steatosis in transgenic mice. J Gen Virol. 1997;78(Pt 7):1527–31. - PubMed
-
- Nunez O, Fernandez-Martinez A, Majano PL, Apolinario A, Gomez-Gonzalo M, Benedicto I, et al. Increased intrahepatic cyclooxygenase 2, matrix metalloproteinase 2, and matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression is associated with progressive liver disease in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: role of viral core and NS5A proteins. Gut. 2004;53:1665–72. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

