Efficacy of an Enrichment Media for Increasing Threshold for Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Screening
- PMID: 26666427
- PMCID: PMC6807085
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21903
Efficacy of an Enrichment Media for Increasing Threshold for Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Screening
Abstract
Background: Identification of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) is complex and a major laboratory challenge; clinical cultures may diagnose only some of the CRE carriers among patients, thus it is crucial to perform asymptomatic carriage screening.
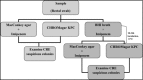
Materials and methods: We compare the efficacy of a rectal sample culture prior to enrichment with BHI (Brain Heart Infusion) Broth and following 18-24 h. All rectal samples were applied on CHROMagar KPC selective growth media and then seeded on MacConkey agar selective growth media with an applied disk of Imipenem antibiotic on top of the media, then inserted into enrichment BHI Broth. After 18-24 h incubation with enrichment media, all samples were applied again on this media.
Results: From the 2,245 rectal samples, CRE colonies were found in 96 (4.3%). Following enrichment with BHI Broth, CRE colonies were found in 111 (4.9%) CHROMagar KPC plates and 106 (4.7%) MacConkey agar.
Conclusion: We were able to demonstrate that the number of CRE-positive results increased due to use of additional enrichment with BHI Broth. Therefore, we recommend applying this method of addition of liquid enrichment media as part of a culture protocol routine for CRE screening.
Keywords: Brain-Heart Infusion Broth; CHROMagar KPC; Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; MacConkey agar.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Gupta N, Limbago BM, Patel JB, Kallen AJ. Carbapenem‐resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Epidemiology and prevention. Clin Infect Dis 2011;53:60–67. - PubMed
-
- Bonomo RA. New Delhi metallo‐β‐lactamase and multidrug resistance: A global SOS? Clin Infect Dis 2011;52:485–487. - PubMed
-
- Hyle EP, Ferraro MJ, Silver M, Lee H, Hooper DC. Ertapenem‐resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Risk factors for acquisition and outcomes. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2010;31:1242–1249. - PubMed
-
- Kwak YG, Choi SH, Choo EJ, et al. Risk factors for the acquisition of carbapenem‐resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae among hospitalized patients. Microb Drug Resist 2005;11:165–169. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical