Role of Intestinal HIF-2α in Health and Disease
- PMID: 26667076
- PMCID: PMC4809193
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105202
Role of Intestinal HIF-2α in Health and Disease
Abstract
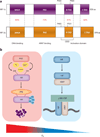
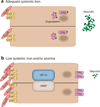
The intestine is supported by a complex vascular system that undergoes dynamic and transient daily shifts in blood perfusion, depending on the metabolic state. Moreover, the intestinal villi have a steep oxygen gradient from the hypoxic epithelium adjacent to the anoxic lumen to the relative higher tissue oxygenation at the base of villi. Due to the daily changes in tissue oxygen levels in the intestine, the hypoxic transcription factors hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-2α are essential in maintaining intestinal homeostasis. HIF-2α is essential in maintaining proper micronutrient balance, the inflammatory response, and the regenerative and proliferative capacity of the intestine following an acute injury. However, chronic activation of HIF-2α leads to enhanced proinflammatory response, intestinal injury, and colorectal cancer. In this review, we detail the major mechanisms by which HIF-2α contributes to health and disease of the intestine and the therapeutic implications of targeting HIF-2α in intestinal diseases.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; colon cancer; hypoxia; inflammatory bowel disease; iron; ulcerative colitis.
Figures


References
-
- Helander HF, Fandriks L. Surface area of the digestive tract—revisited. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014;49:681–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

