Activator of G-Protein Signaling 3-Induced Lysosomal Biogenesis Limits Macrophage Intracellular Bacterial Infection
- PMID: 26667172
- PMCID: PMC4811337
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501595
Activator of G-Protein Signaling 3-Induced Lysosomal Biogenesis Limits Macrophage Intracellular Bacterial Infection
Abstract
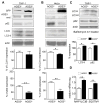
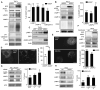
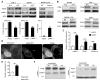
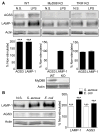
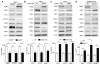
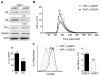
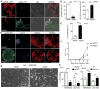
Many intracellular pathogens cause disease by subverting macrophage innate immune defense mechanisms. Intracellular pathogens actively avoid delivery to or directly target lysosomes, the major intracellular degradative organelle. In this article, we demonstrate that activator of G-protein signaling 3 (AGS3), an LPS-inducible protein in macrophages, affects both lysosomal biogenesis and activity. AGS3 binds the Gi family of G proteins via its G-protein regulatory (GoLoco) motif, stabilizing the Gα subunit in its GDP-bound conformation. Elevated AGS3 levels in macrophages limited the activity of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway, a sensor of cellular nutritional status. This triggered the nuclear translocation of transcription factor EB, a known activator of lysosomal gene transcription. In contrast, AGS3-deficient macrophages had increased mammalian target of rapamycin activity, reduced transcription factor EB activity, and a lower lysosomal mass. High levels of AGS3 in macrophages enhanced their resistance to infection by Burkholderia cenocepacia J2315, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, whereas AGS3-deficient macrophages were more susceptible. We conclude that LPS priming increases AGS3 levels, which enhances lysosomal function and increases the capacity of macrophages to eliminate intracellular pathogens.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activator of G protein signaling 3 is a guanine dissociation inhibitor for Galpha i subunits.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14364-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.26.14364. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11121039 Free PMC article.
-
Normal autophagic activity in macrophages from mice lacking Gαi3, AGS3, or RGS19.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 28;8(11):e81886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081886. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24312373 Free PMC article.
-
Ric-8A catalyzes guanine nucleotide exchange on G alphai1 bound to the GPR/GoLoco exchange inhibitor AGS3.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 22;283(34):23150-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802422200. Epub 2008 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18541531 Free PMC article.
-
Activators of G-protein signaling 3: a drug addiction molecular gateway.Behav Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;21(5-6):500-13. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32833dcfa5. Behav Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20700046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial responses of teleost phagocytes and innate immune evasion strategies of intracellular bacteria.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Apr;43(2):223-42. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 23954721 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of G-proteins and phosphorylation in the distribution of AGS3 to cell puncta.J Cell Sci. 2018 Dec 5;131(23):jcs216507. doi: 10.1242/jcs.216507. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404823 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of GPSM1 Inhibits the Proliferation and Promotes the Apoptosis of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells by Suppressing the ADCY6-RAPGEF3-JNK Signaling Pathway.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Apr 7;27:643376. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.643376. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34257610 Free PMC article.
-
The Transcription Factor EB Links Cellular Stress to the Immune Response .Yale J Biol Med. 2017 Jun 23;90(2):301-315. eCollection 2017 Jun. Yale J Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28656016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of RGS and other G-protein regulatory proteins on Gαi-mediated signaling in immunity.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 15;114:40-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27071343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gαi2 Signaling Regulates Inflammasome Priming and Cytokine Production by Biasing Macrophage Phenotype Determination.J Immunol. 2019 Mar 1;202(5):1510-1520. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801145. Epub 2019 Jan 25. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30683698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baxt LA, Garza-Mayers AC, Goldberg MB. Bacterial subversion of host innate immune pathways. Science. 2013;340:697–701. - PubMed
-
- Schwegmann A, Brombacher F. Host-directed drug targeting of factors hijacked by pathogens. Science signaling. 2008;1:re8. - PubMed
-
- Lebeis SL, Kalman D. Aligning antimicrobial drug discovery with complex and redundant host-pathogen interactions. Cell host & microbe. 2009;5:114–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

