A comprehensive analysis of radiosensitization targets; functional inhibition of DNA methyltransferase 3B radiosensitizes by disrupting DNA damage regulation
- PMID: 26667181
- PMCID: PMC4678329
- DOI: 10.1038/srep18231
A comprehensive analysis of radiosensitization targets; functional inhibition of DNA methyltransferase 3B radiosensitizes by disrupting DNA damage regulation
Abstract
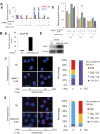
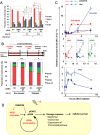
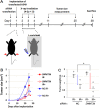
A comprehensive genome-wide screen of radiosensitization targets in HeLa cells was performed using a shRNA-library/functional cluster analysis and DNMT3B was identified as a candidate target. DNMT3B RNAi increased the sensitivity of HeLa, A549 and HCT116 cells to both γ-irradiation and carbon-ion beam irradiation. DNMT3B RNAi reduced the activation of DNA damage responses induced by γ-irradiation, including HP1β-, γH2AX- and Rad51-foci formation. DNMT3B RNAi impaired damage-dependent H2AX accumulation and showed a reduced level of γH2AX induction after γ-irradiation. DNMT3B interacted with HP1β in non-irradiated conditions, whereas irradiation abrogated the DNMT3B/HP1β complex but induced interaction between DNMT3B and H2AX. Consistent with radiosensitization, TP63, BAX, PUMA and NOXA expression was induced after γ-irradiation in DNMT3B knockdown cells. Together with the observation that H2AX overexpression canceled radiosensitization by DNMT3B RNAi, these results suggest that DNMT3B RNAi induced radiosensitization through impairment of damage-dependent HP1β foci formation and efficient γH2AX-induction mechanisms including H2AX accumulation. Enhanced radiosensitivity by DNMT3B RNAi was also observed in a tumor xenograft model. Taken together, the current study implies that comprehensive screening accompanied by a cluster analysis enabled the identification of radiosensitization targets. Downregulation of DNMT3B, one of the targets identified using this method, radiosensitizes cancer cells by disturbing multiple DNA damage responses.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cyclin D1 silencing suppresses tumorigenicity, impairs DNA double strand break repair and thus radiosensitizes androgen-independent prostate cancer cells to DNA damage.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 2;7(5):5383-400. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6579. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26689991 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Annexin A1 Enhances Radioresistance and Inhibits Apoptosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jan 1;17:1533034617750309. doi: 10.1177/1533034617750309. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29357787 Free PMC article.
-
A small interfering RNA screen of genes involved in DNA repair identifies tumor-specific radiosensitization by POLQ knockdown.Cancer Res. 2010 Apr 1;70(7):2984-93. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4040. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20233878 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference to enhance radiation therapy: Targeting the DNA damage response.Cancer Lett. 2018 Dec 28;439:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 30240587 Review.
-
PP2A and tumor radiotherapy.Hereditas. 2020 Aug 26;157(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s41065-020-00149-7. Hereditas. 2020. PMID: 32847617 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-29b-3p Increases Radiosensitivity in Stemness Cancer Cells via Modulating Oncogenes Axis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 16;9:741074. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.741074. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34604239 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Functional Inhibition of BACE1 on Sensitization to γ-Irradiation in Cancer Cells.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 2;46(1):450-460. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010028. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38248330 Free PMC article.
-
Up- regulation of miR-328-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer to radiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 17;6:31651. doi: 10.1038/srep31651. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27530148 Free PMC article.
-
Cross resistance to diverse anticancer nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase inhibitors induced by FK866 treatment.Oncotarget. 2018 Mar 27;9(23):16451-16461. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24731. eCollection 2018 Mar 27. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29662658 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitization to γ-Ray by Functional Inhibition of APOBEC3G.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 3;23(9):5069. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095069. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freytag S. O., Rogulski K. R., Paielli D. L., Gilbert J. D. & Kim J. H. A novel three-pronged approach to kill cancer cells selectively: concomitant viral, double suicide gene, and radiotherapy. Human gene therapy 9, 1323–1333 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Daido S. et al. Inhibition of the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit radiosensitizes malignant glioma cells by inducing autophagy. Cancer Res 65, 4368–4375 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Schlicker A., Peschke P., Burkle A., Hahn E. W. & Kim J. H. 4-Amino-1,8-naphthalimide: a novel inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and radiation sensitizer. Int J Radiat Biol 75, 91–100 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Shirai H. et al. Parg deficiency confers radio-sensitization through enhanced cell death in mouse ES cells exposed to various forms of ionizing radiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435, 100–106 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Sorensen C. S. et al. The cell-cycle checkpoint kinase Chk1 is required for mammalian homologous recombination repair. Nat Cell Biol 7, 195–201 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

