Unexpected Delayed Colon Perforation after the Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection with Snaring of a Laterally Spreading Tumor
- PMID: 26668808
- PMCID: PMC4676666
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2015.48.6.570
Unexpected Delayed Colon Perforation after the Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection with Snaring of a Laterally Spreading Tumor
Abstract
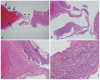
Colonic perforation may occur as a complication of diagnostic and therapeutic colonoscopy. The risk factors for perforation after colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) include an inexperienced endoscopist, a large tumor size, and submucosal fibrosis. The mechanisms of perforation include unintended endoscopic resection/dissection and severe thermal injury. Here, we report a case of colon perforation that occurred after ESD with snaring of a laterally spreading tumor. The perforation was completely unexpected because there were no colorectal ESD-associated risk factors for perforation, deep dissection, or severe coagulation injury in our patient.
Keywords: Delayed perforation; Endoscopic submucosal dissection; Mechanism; Risk factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Raju GS, Saito Y, Matsuda T, Kaltenbach T, Soetikno R. Endoscopic management of colonoscopic perforations (with videos) Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:1380–1388. - PubMed
-
- Panteris V, Haringsma J, Kuipers EJ. Colonoscopy perforation rate, mechanisms and outcome: from diagnostic to therapeutic colonoscopy. Endoscopy. 2009;41:941–951. - PubMed
-
- Mizushima T, Kato M, Iwanaga I, et al. Technical difficulty according to location, and risk factors for perforation, in endoscopic submucosal dissection of colorectal tumors. Surg Endosc. 2015;29:133–139. - PubMed
-
- Isomoto H, Nishiyama H, Yamaguchi N, et al. Clinicopathological factors associated with clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy. 2009;41:679–683. - PubMed
-
- Xiao YF, Bai JY, Yu J, et al. Endoscopic treatment of delayed colon perforation: the enteroscopy overtube approach. Endoscopy. 2014;46:503–508. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

