Casein kinase II promotes target silencing by miRISC through direct phosphorylation of the DEAD-box RNA helicase CGH-1
- PMID: 26669440
- PMCID: PMC4702986
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1509499112
Casein kinase II promotes target silencing by miRISC through direct phosphorylation of the DEAD-box RNA helicase CGH-1
Erratum in
-
Correction to Supporting Information for Alessi et al., Casein kinase II promotes target silencing by miRISC through direct phosphorylation of the DEAD-box RNA helicase CGH-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 16;113(7):E942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600214113. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26858445 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
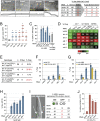
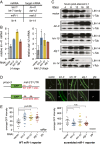
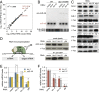
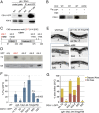
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play essential, conserved roles in diverse developmental processes through association with the miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC). Whereas fundamental insights into the mechanistic framework of miRNA biogenesis and target gene silencing have been established, posttranslational modifications that affect miRISC function are less well understood. Here we report that the conserved serine/threonine kinase, casein kinase II (CK2), promotes miRISC function in Caenorhabditis elegans. CK2 inactivation results in developmental defects that phenocopy loss of miRISC cofactors and enhances the loss of miRNA function in diverse cellular contexts. Whereas CK2 is dispensable for miRNA biogenesis and the stability of miRISC cofactors, it is required for efficient miRISC target mRNA binding and silencing. Importantly, we identify the conserved DEAD-box RNA helicase, CGH-1/DDX6, as a key CK2 substrate within miRISC and demonstrate phosphorylation of a conserved N-terminal serine is required for CGH-1 function in the miRNA pathway.
Keywords: CGH-1; casein kinase II; miRISC; microRNA; phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Reinhart BJ, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403(6772):901–906. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

